
3D printing of houses is becoming real — with the help of construction 3D printers, buildings are printed in Russia, China, Europe, Asia and America. In this article, we’ll talk about the most promising projects in the field.
Let’s start with the technology. The principle of construction 3D printers is the extrusion of special mixture, layer by layer, according to a given three-dimensional computer model.
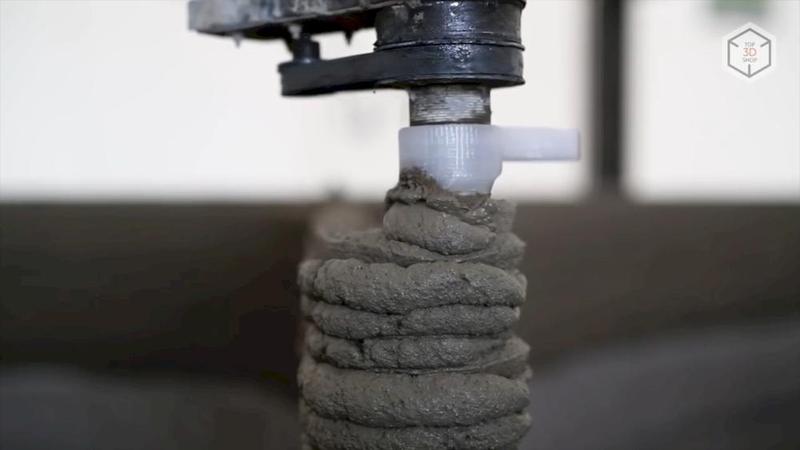

Pre-prepared mixture consisting of cement, filler, plasticizer and other additives is loaded into the hopper of the device and fed to the printhead. The mixture is applied to the surface of the site or previously printed layers.

Most construction 3D printers work on that principle. There are three types of devices among them:
Gantry 3D printers are a construction of a frame, three gantries and a printhead. With the help of such devices, it is possible to print buildings either in parts or in whole (if they fit under the arch of the printer).

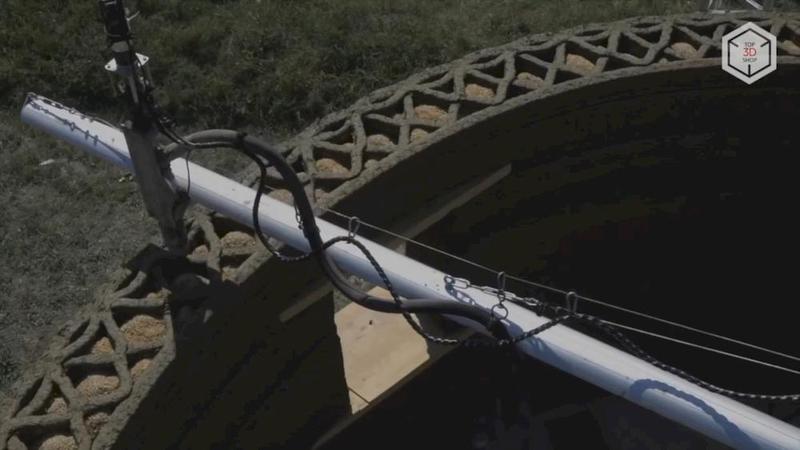
Delta devices are independent of three-dimensional guides, and can print more complex shapes. Here, the printhead is suspended at levers which are attached to vertical guides.

Finally, robotic printers are a robot or a system of robots such as an industrial manipulator equipped with extruders and controlled by a computer.
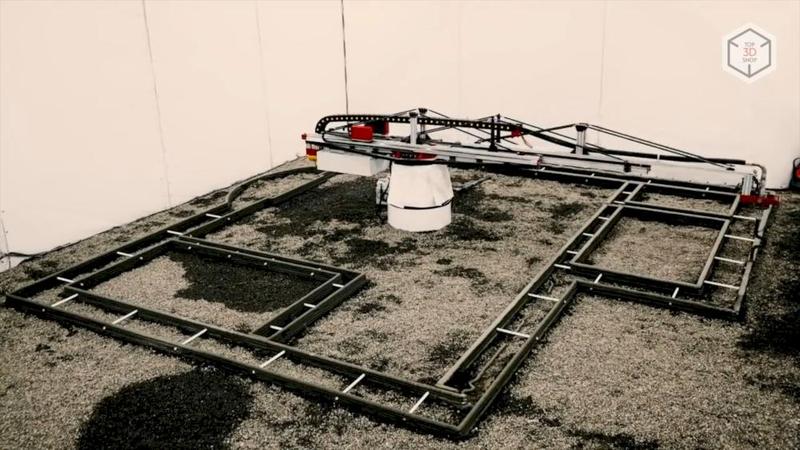

There are also other methods of construction 3D printing. For example: D-Shape equipment prints by layering with powder material and bonding it by applying adhesive solution.
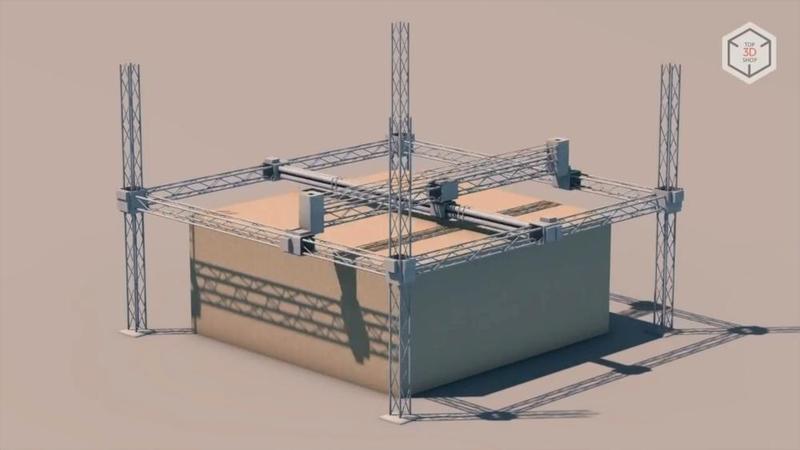
The main material for 3D printing of houses is fine-grained mixtures, which differ from traditional concrete. Each company develops its own recipe appropriate for the structure of a printer and its nozzle as well as the specifics of finished products.
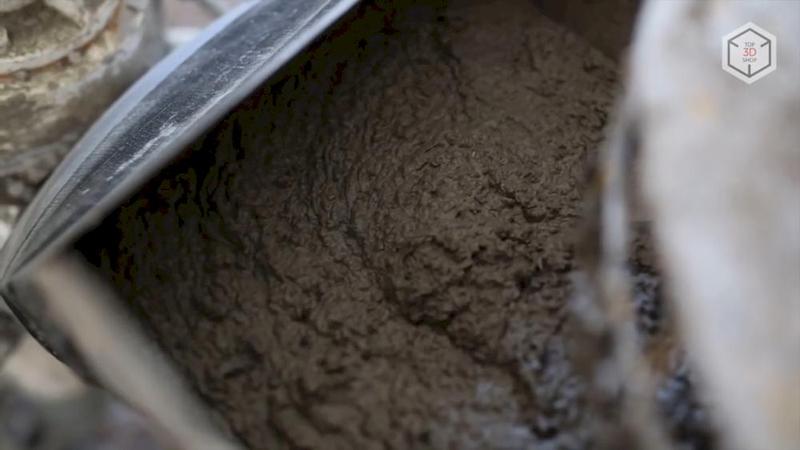

The most important specifications of concrete for a 3D printer are durability, speed of solidification and setting, ductility. The properties of concrete are regulated by the composition of the mixture — the amount of cement and the quality of fillers, as well as the additives of plasticizers.
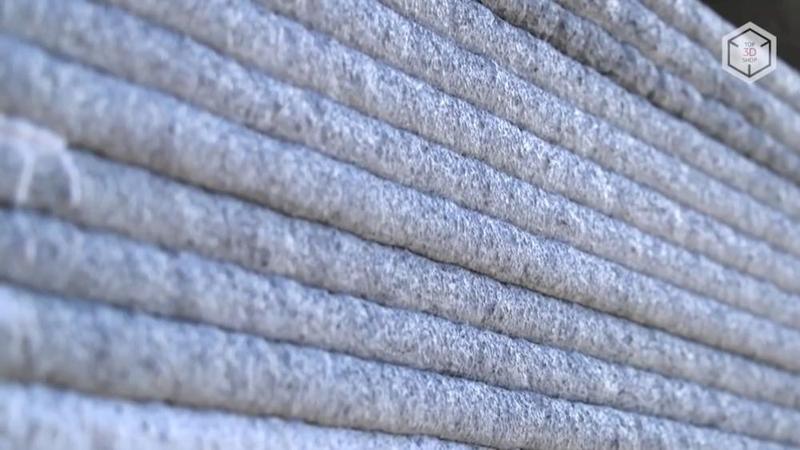

Ready mixtures allow you to print elements of various complexity and sizes — from small architectural forms such as flower beds and benches to entire buildings, bridges and even skyscrapers.
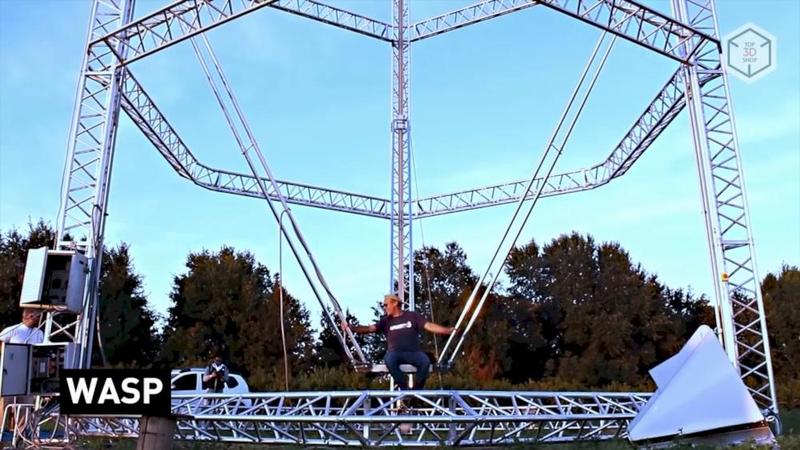


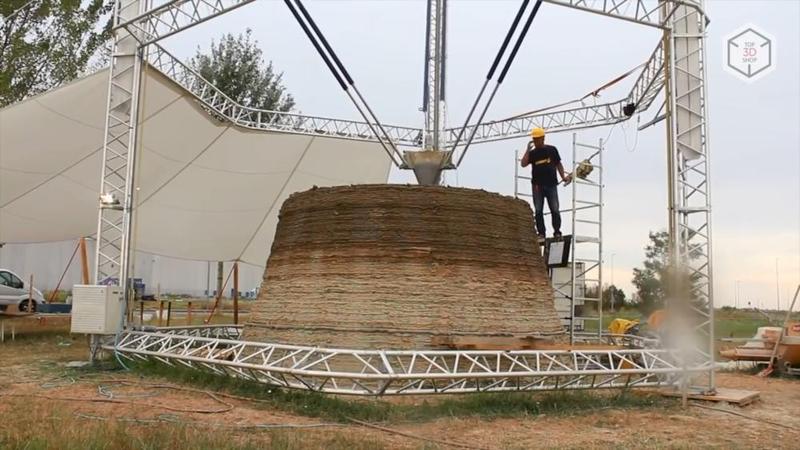
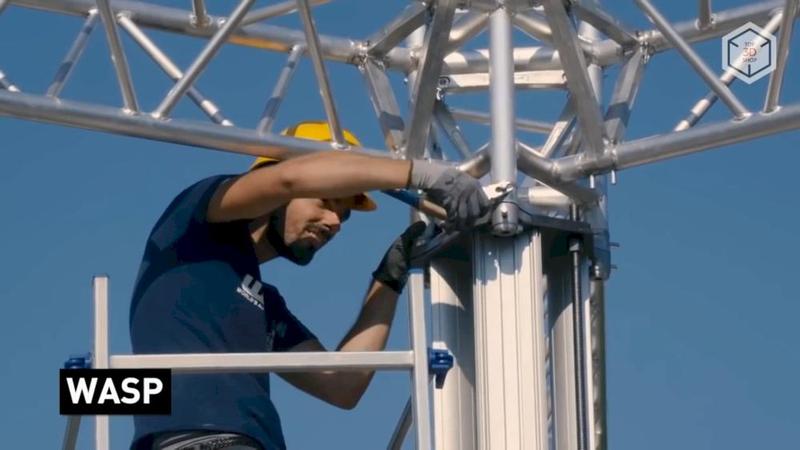
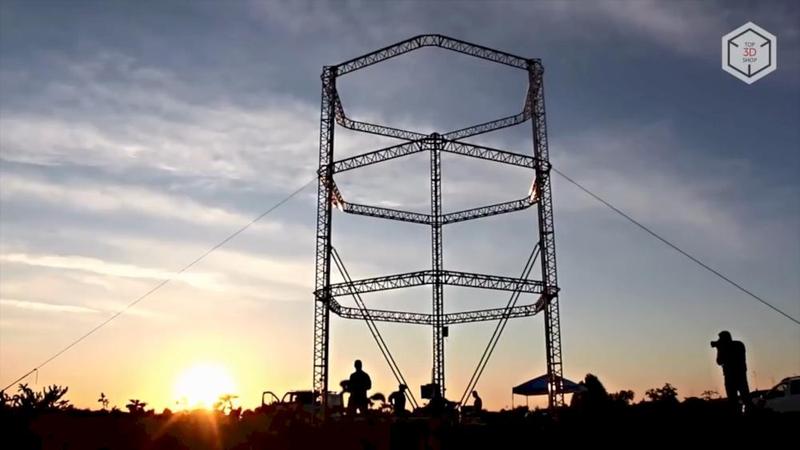
The WASP Italian manufacturer has created the largest construction 3D printer to date. This delta bot, 12 meters high and 7 meters wide, has adjustable levers up to 6 meters long.

The use of a printer called BigDelta is aimed at eliminating the housing crisis by creating cheaper houses, which is especially important for developing countries.

The BigDelta project is construction 3D printing with the use of natural materials. As "consumables", the project uses pressed straw and soil.
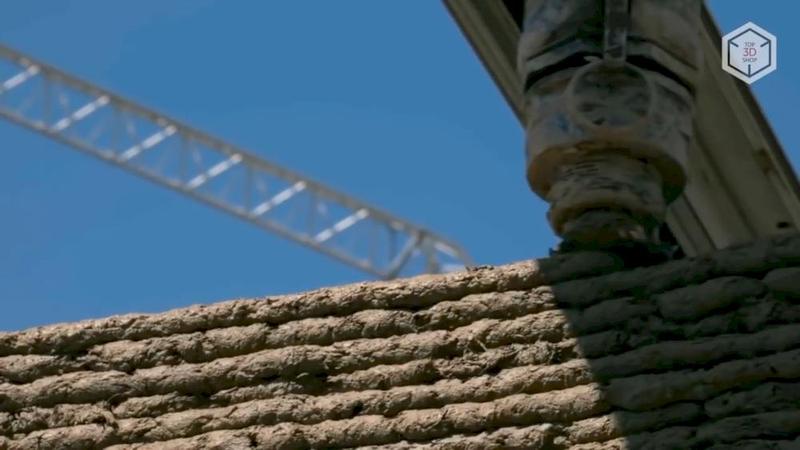
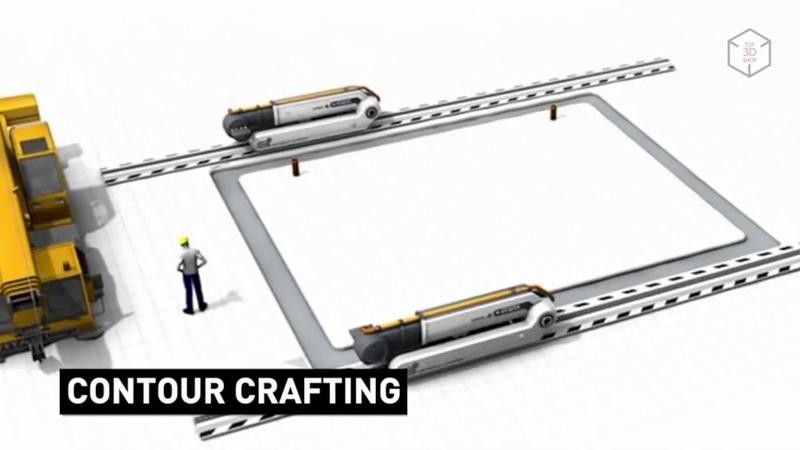


In 2009, residents of the Singularity University startup incubator (aka Singularity Education Group, founded in 2008 at NASA Research Park, California) under the leadership of Behrokh Khoshnevis created a project for the development and commercial application of contouring construction technology — Contour Crafting, which is considered the first construction technology for 3D printing and has actually become the most common one — this is the very technology in which cement mixture is applied by an extruder, like plastic when printing with FDM.
Founded by Behrokh Khoshnevis, the eponymous company develops this 3D printing technology and collaborates with NASA. The developer suggests using this printing method to restore cities affected by natural disasters and to build structures on other planets.

The company uses a computer-controlled gantry crane with an extruder mounted on it for 3D printing of buildings. The Contour Crafting process involves quick-set materialб which is applied by the crane in layers. Technical elements such as fittings and communications can be added as layers are created.
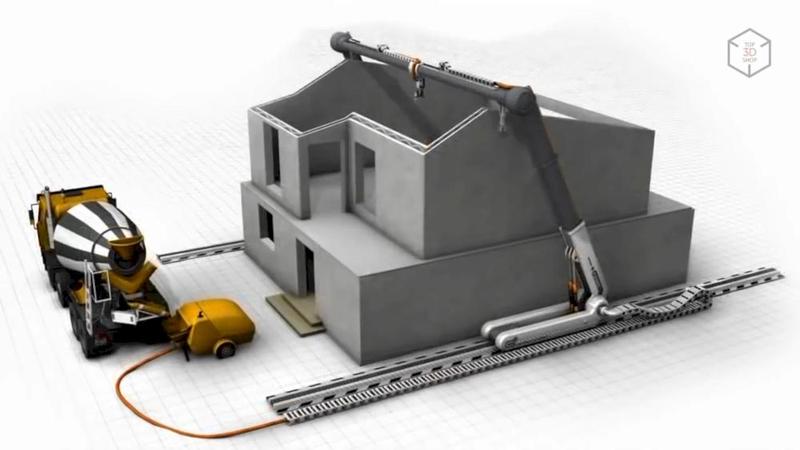

The AMT is part of the AMT-SPETSAVIA group of companies. Its area of activity is the development and manufacture of construction 3D printers, sale and maintenance of equipment in the world market. The company's product range consists of seven 3D printers of different sizes.
This house in Yaroslavl is the largest building in Europe and the CIS that was built using AMT printers. Its total floor space is 298 square meters.
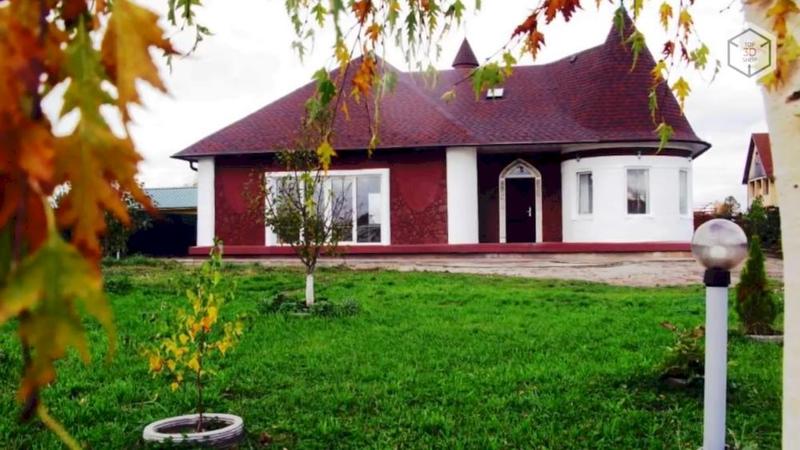

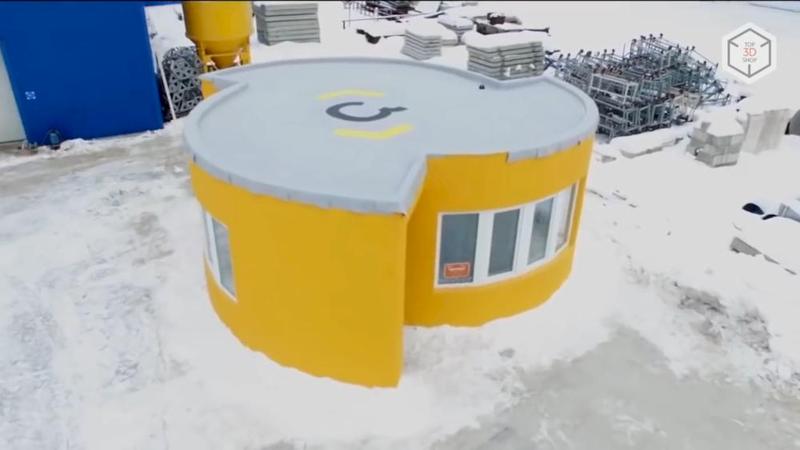
The Apis Cor Engineering company is a Russian developer of a unique mobile 3D device that can print a house entirely at the construction site.
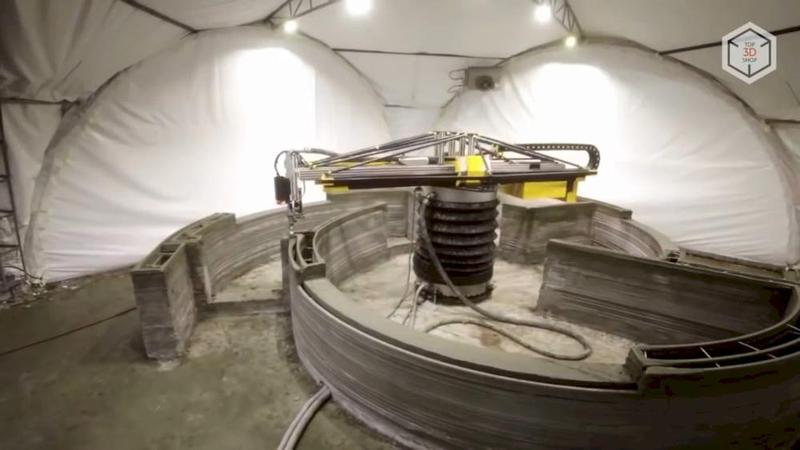

The overall dimensions of the 3D printer when assembled are 4×1.6×1.5m, the weight is 2 tons. The print zone is 131 square meters. To print buildings and structures of large sizes, several synchronized 3D printers can be used.

In 2014, the Shanghai-based Winsun company became famous worldwide for the construction of ten 3D-printed buildings in just one day. In fact, things turned out to be a little more modest: small “boxes” were printed block by block in advance and then assembled at the construction site, without fittings and communications, but with glazing.
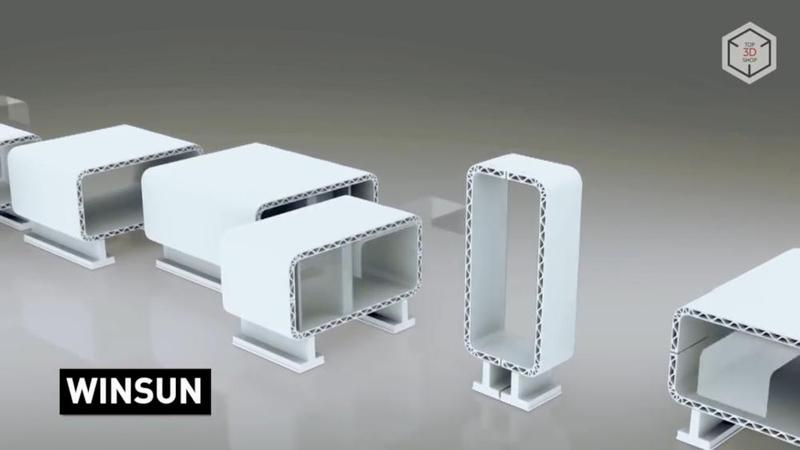
The company uses a printer based on FDM technology and incremental process with cement, sand and fiberglass. These materials provide sufficient wall strength. The WINSUN 3D printer has a gantry design with dimensions of 36x12x6 meters.

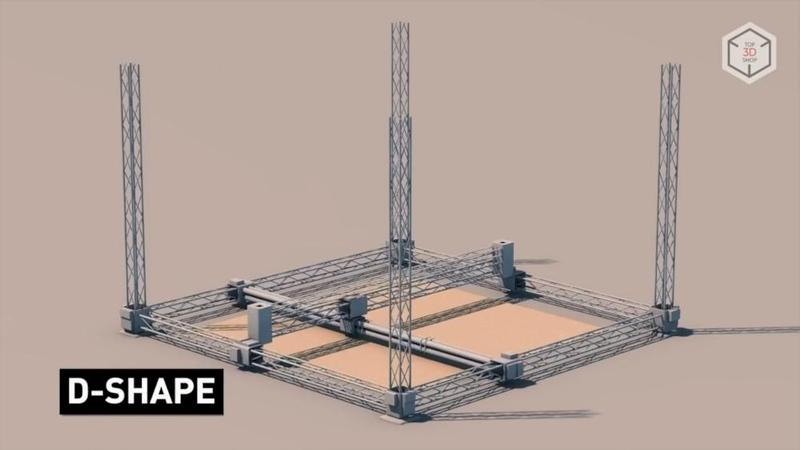
D-Shape is one of the most unusual options for construction 3D printing. The device does not use an extruder positioned along three axes, but relies on an array of 300 nozzles mounted on a movable platform. The dimensions of the printer’s platform in the current version are 6x6 meters.
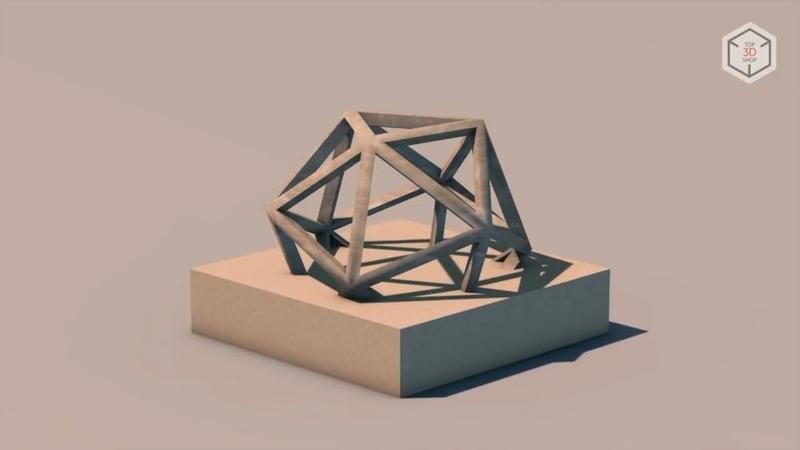

The D-Shape technology resembles inkjet printing; the set of nozzles is used to apply a bonding agent to sand layers.
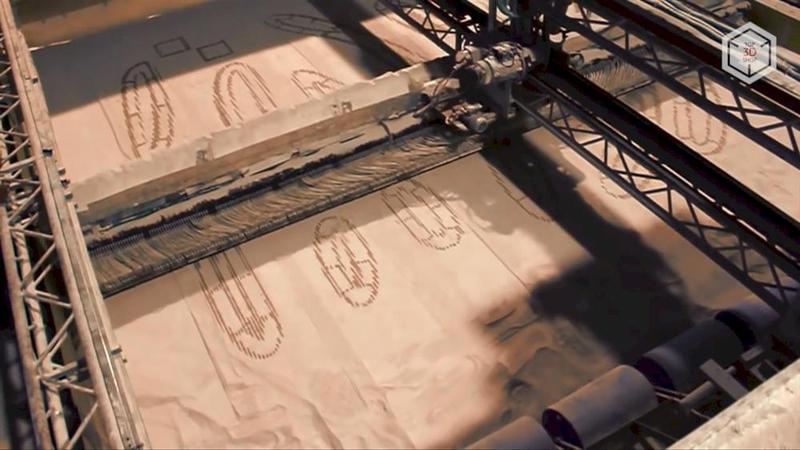


CyBe Construction is a company from the Netherlands that uses 3D printing in the "turnkey" construction of houses. CyBe produces building materials and two models of construction 3D printers.
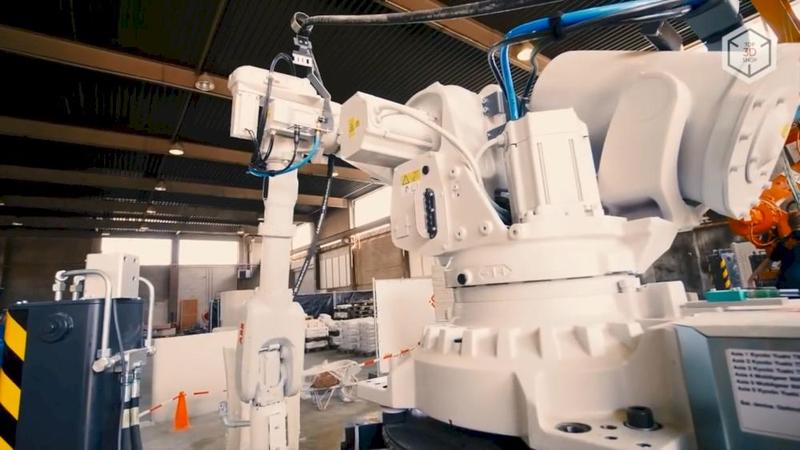

These large industrial devices require the participation of two operators, however, they are capable of printing large buildings very quickly. For example, in Dubai in 2017, the company printed a 168-square-meter laboratory in just three weeks.
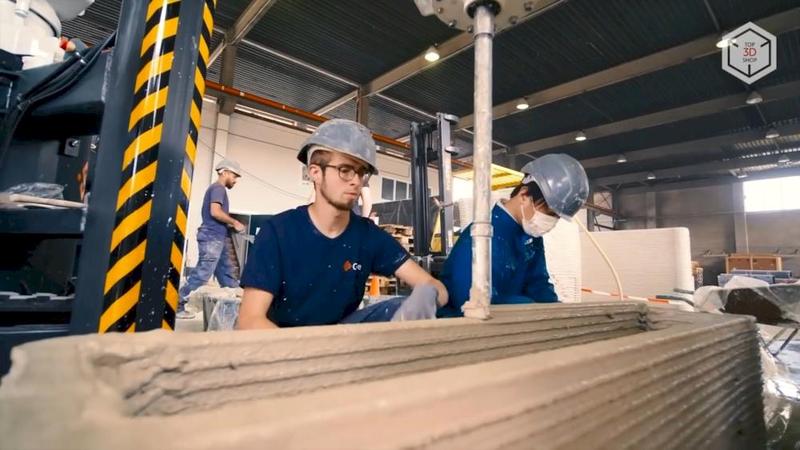
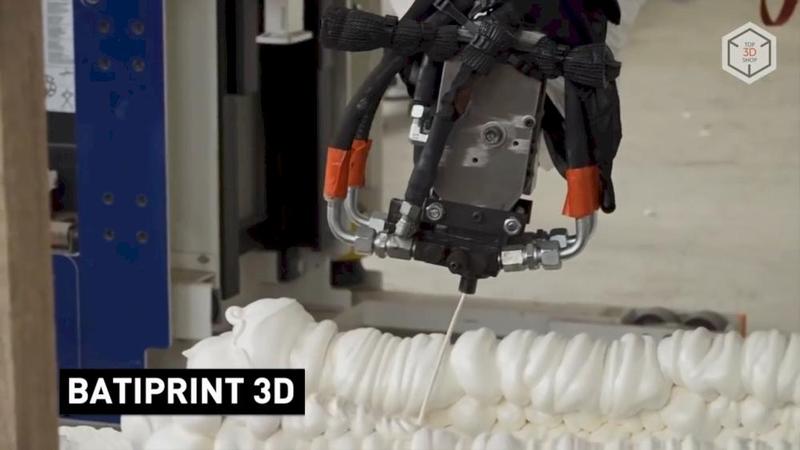


The University of Nantes, France, in collaboration with the Laboratory of Digital Sciences of Nantes (LS2N), is working on a 3D printed house project known as Yhnova.
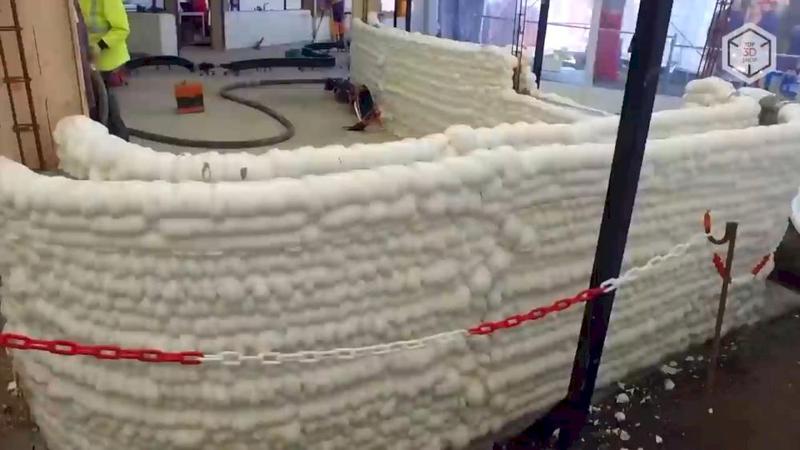

The Batiprint3D method developed by the university will be used for the project — 3D printing "from the inside". Polyurethane formwork is printed with the help of layer-by-layer spraying of material similar to fixing foam, after hardening of which it is filled with concrete.
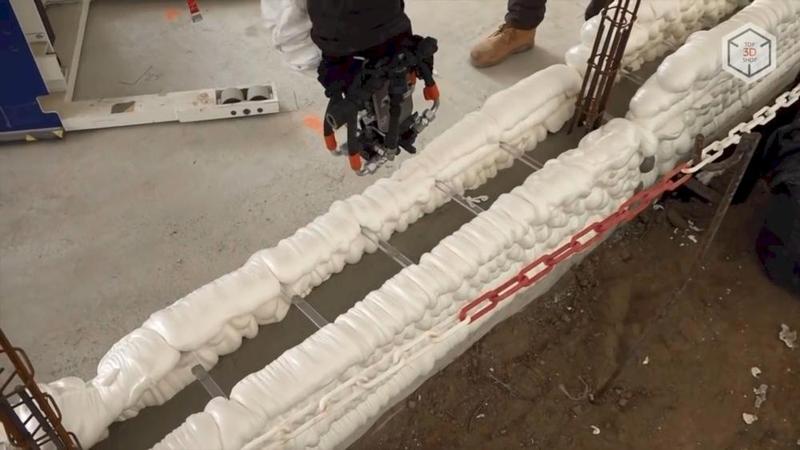

The Yhnova project is the construction of a five-room social housing with arched walls and rounded corners. The Batiprint3D robotic arm can print structures up to 7 meters high, and the area of the planned house is 95 square meters.
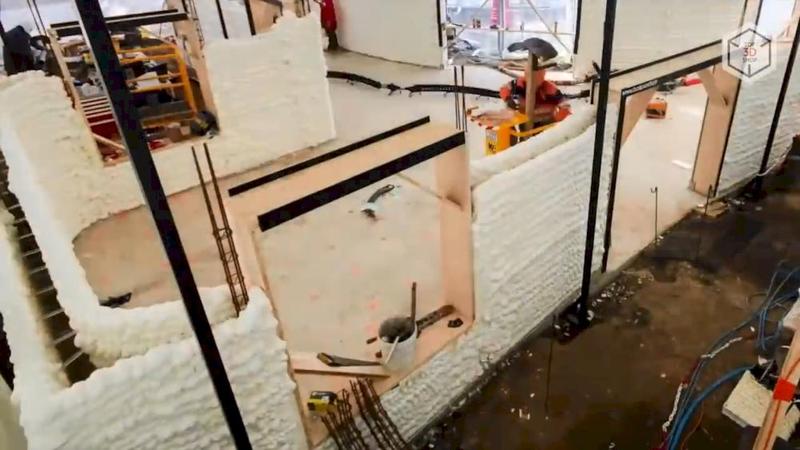

Construction 3D printing is one of the most promising areas in construction as a whole. Its application leads to commercial benefits based on fewer staff needed and lower material costs; social benefits — due to the ability to quickly build low-cost housing for the poor and those affected by natural disasters; reputation bonuses — more environmentally friendly construction with reduced energy consumption and waste.
Contact Top 3D Shop for the acquisition of construction 3D printing equipment and the rational integration of additive technologies into your business process, our managers and engineers will give you comprehensive advice on how to use of the equipment, suggest application scenarios, draw up project documentation for delivery and provide qualified service.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment