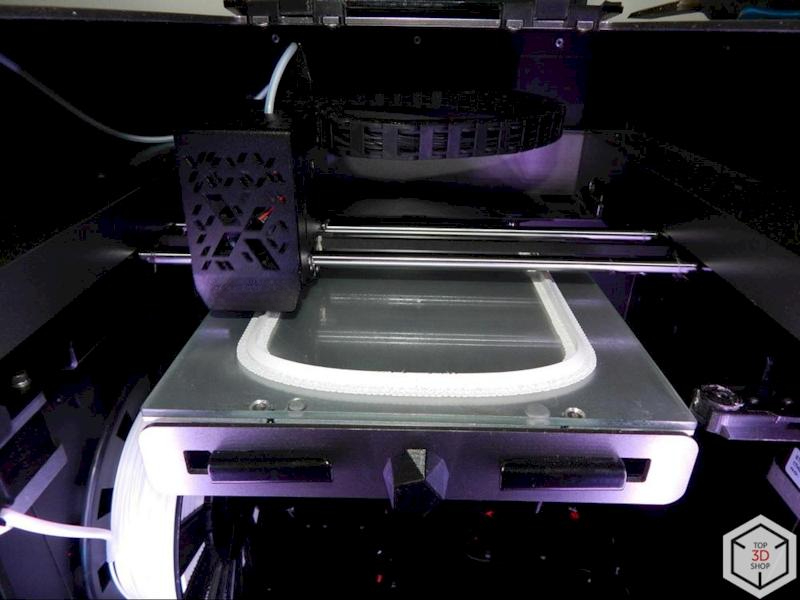
The Epitum 3D printer delivers high throughput and supports a wide range of materials, which is important for producing larger structural components and batches of repetitive parts in architectural models.
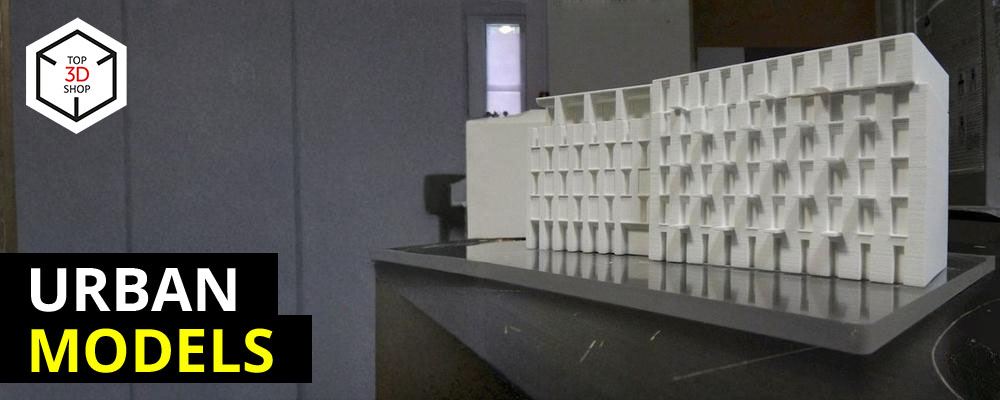

In this article, we explore how a professional model-making studio uses a small 3D printer farm to increase production speed, accuracy, and scalability for city and architectural models.
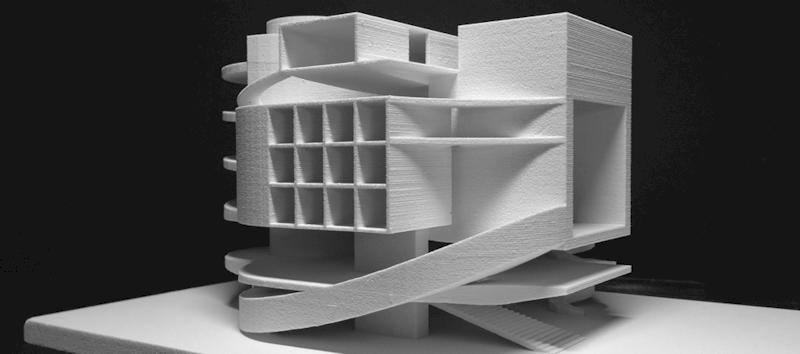
The studio has been producing architectural, industrial, interior, and conceptual models for more than five years, at scales from 1:10 to 1:2000. Their clients include:
Architects
Developers
Museums
Creative agencies
All production takes place in-house. The studio can run several projects at the same time without sacrificing quality, which makes scalability one of its main strengths. 3D printing plays a key role in this capability.
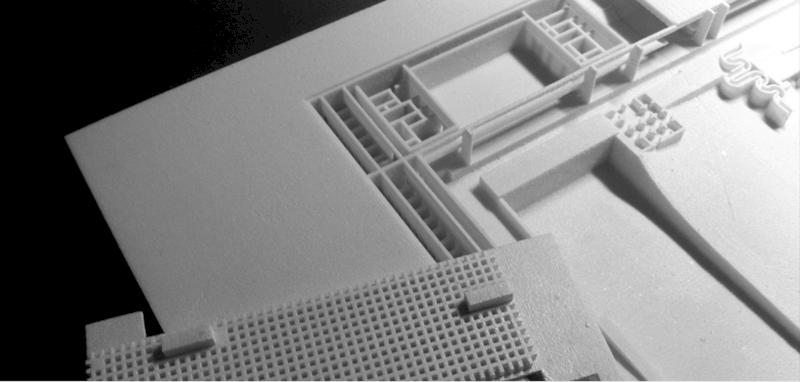
The studio operates five Epitum FDM printers and one Formlabs Form 2 SLA printer, forming a compact but effective print farm.


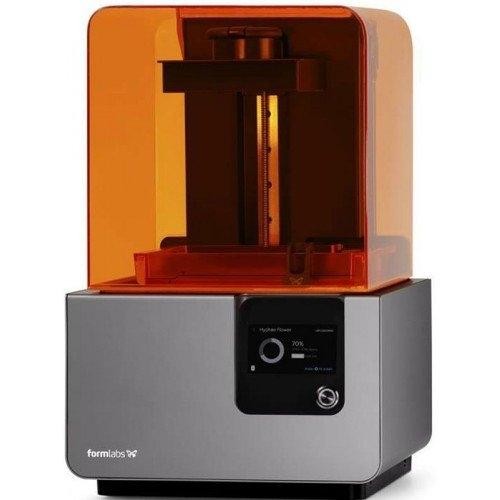
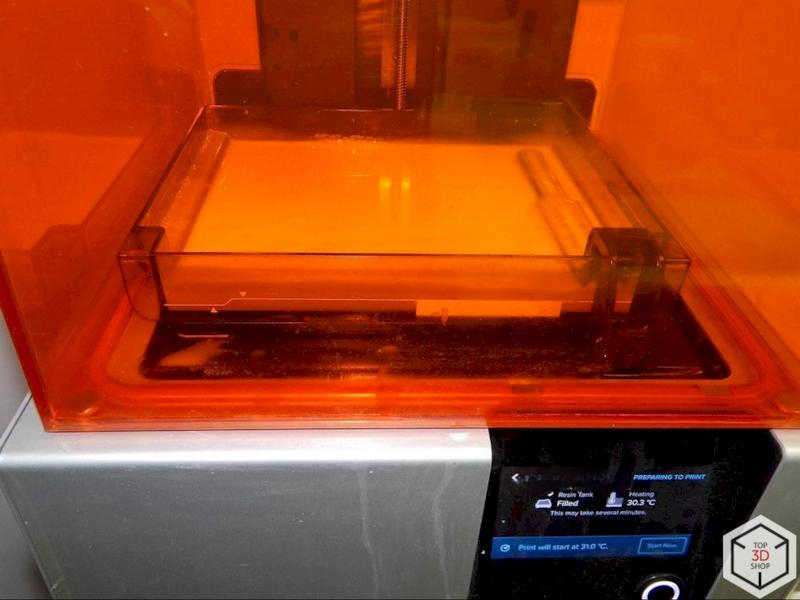
The Formlabs Form 2 provides high precision and fine surface quality, which is important for small architectural details and elements at very small scales.

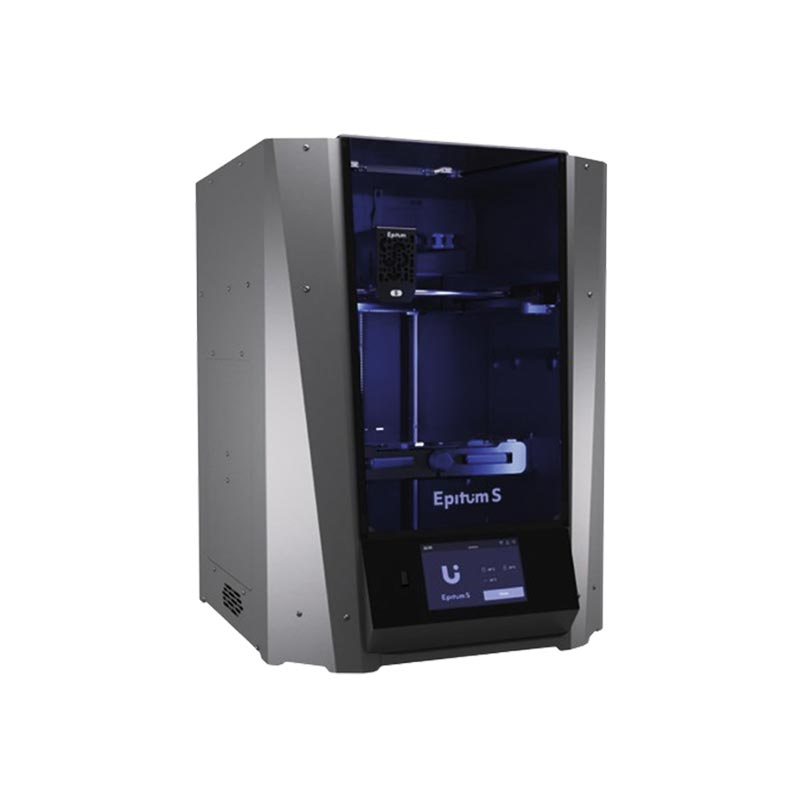
The Epitum 3D printer delivers high throughput and supports a wide range of materials, which is important for producing larger structural components and batches of repetitive parts in architectural models.

The studio divides tasks between the printers:
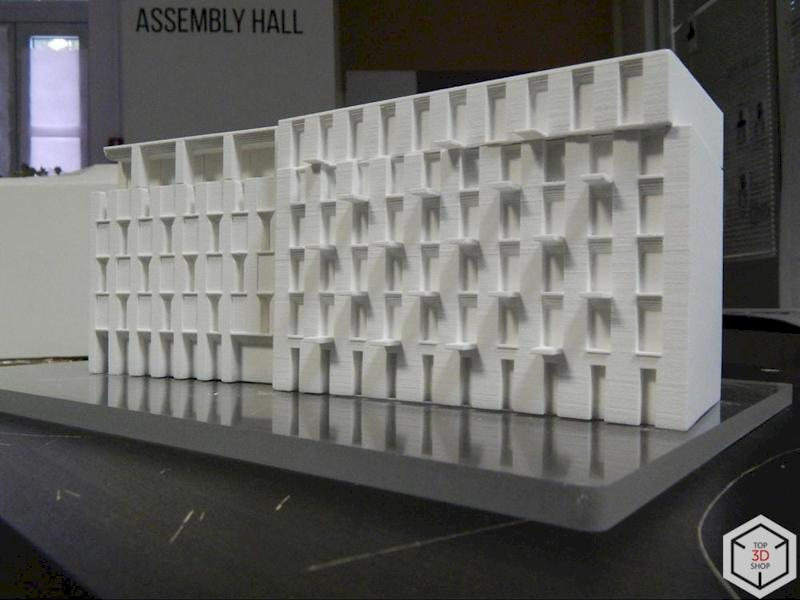
FDM (Epitum) printers – produce larger parts and structural elements.
SLA (Formlabs Form 2) – prints small, highly detailed components that require high resolution.
Typical printed parts include:
Building volumes and structural blocks
Facades and rooftop details
Small decorative elements and urban furniture
Complex shapes that are difficult to cut or mill manually
This combination lets the studio build large city models by assembling many precisely printed parts.


The team chose the Form 2 because of:
Intuitive and stable software
High build quality
Excellent price-to-quality ratio at the time of purchase
It became their main tool for fine details at small scales.

They selected Epitum printers for:
Simple maintenance
High uptime during continuous work
High part throughput and good speed
By running five Epitum printers in parallel, the studio can scale production when a project requires many similar elements.

Before they introduced 3D printing, the studio created components:
By hand, using foam, plastics, and stone
With CNC milling for flat and prismatic parts
These methods are still in use today, but 3D printing significantly expanded what the studio can do.
Many parts that the team now prints on the SLA machine were previously:
Too intricate to make by hand
Too expensive or time-consuming to produce
Not repeatable with consistent quality
Now, they can print such elements with high precision and reproduce them when needed.
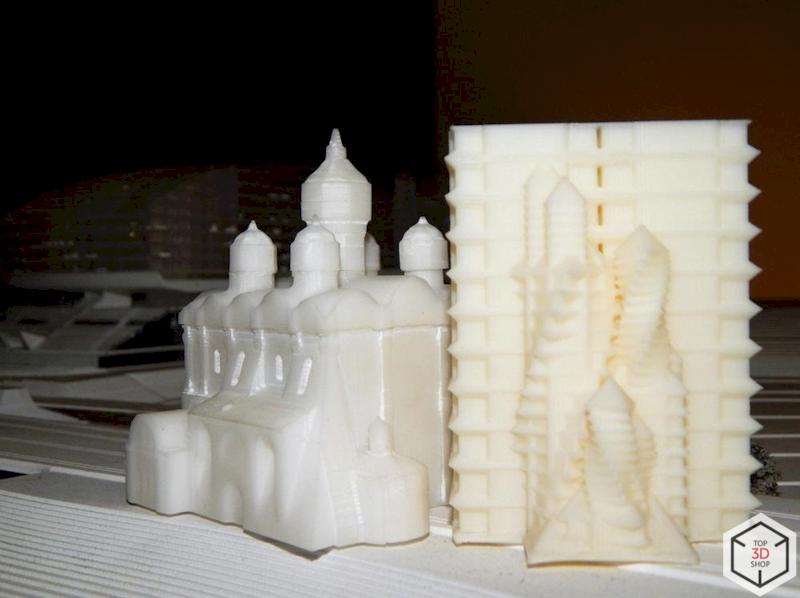

FDM printers give the studio strong benefits in scaling production:
Multiple printers work at the same time
Large batches of components can be produced in parallel
Lead times shrink when several machines share the load
This makes FDM ideal for:
Large structural parts
Repetitive elements in city and masterplan models
Small-batch manufacturing of building volumes
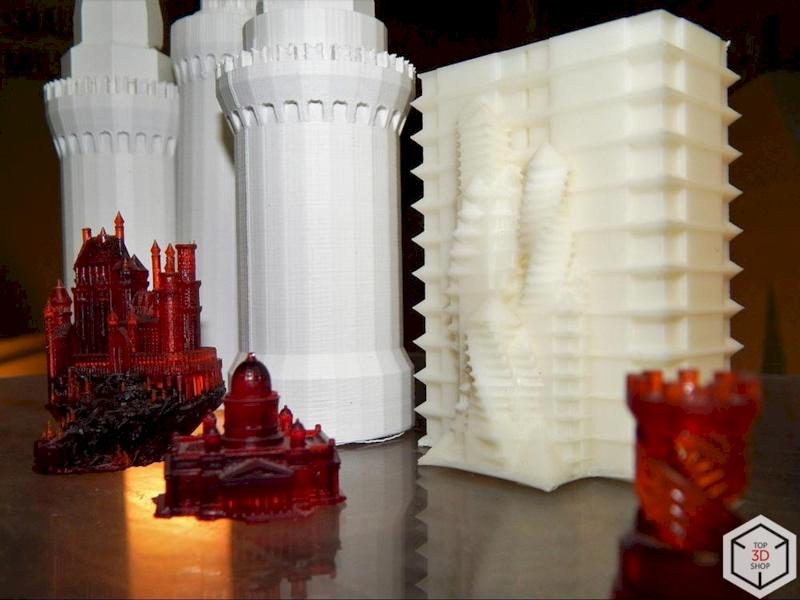
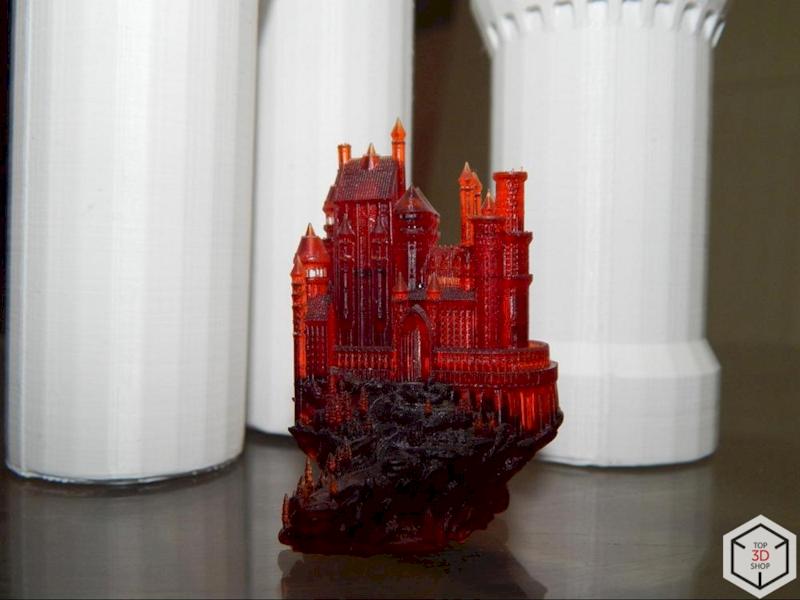
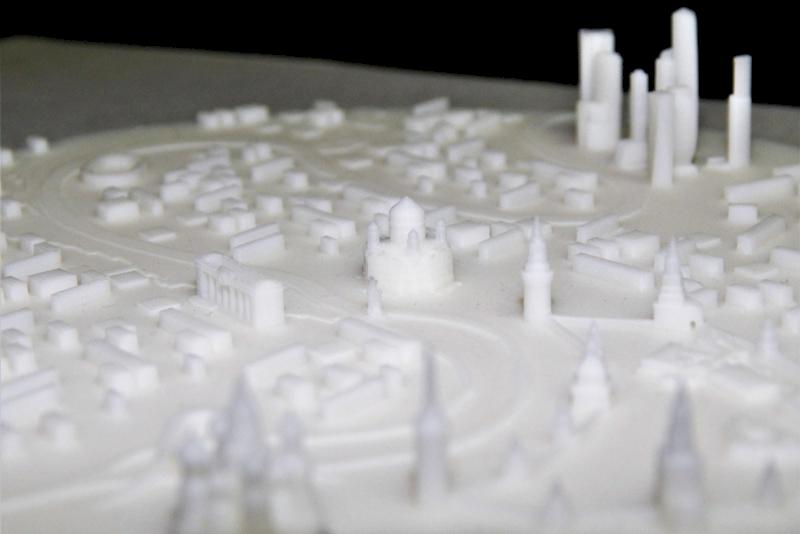
SLA printing allows the studio to work at very small scales, such as 1:1000 or 1:2000, where manual methods and FDM struggle.
With SLA, they can:
Print detailed facades and rooftops
Reproduce fine elements like:
Spires on Gothic cathedrals
Window frames on skyscrapers
Maintain clarity even on tiny features
This level of detail was previously impossible or not economically viable with manual sculpting or CNC alone.
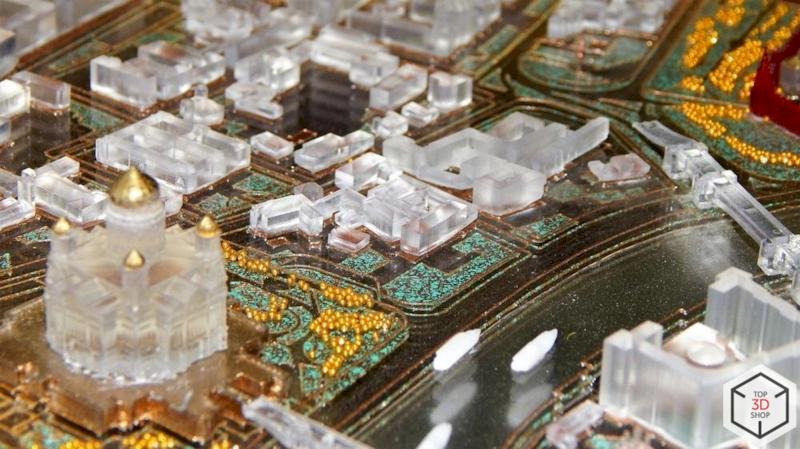


Despite the advantages, 3D printing does not replace every technique.
For large, smooth parts where the surface finish is critical, traditional methods often work better:
FDM leaves visible layer lines that require extensive sanding and finishing.
Heavy post-processing reduces accuracy and increases overall production time.
SLA, although more precise, becomes too slow and expensive for large parts.
For example:
Simple geometric shapes like large building facades are still faster and easier to produce manually from sheet materials or with CNC.
The studio chooses the method (manual, CNC, FDM, or SLA) based on:
Part size
Required surface quality
Level of detail
Budget and deadlines
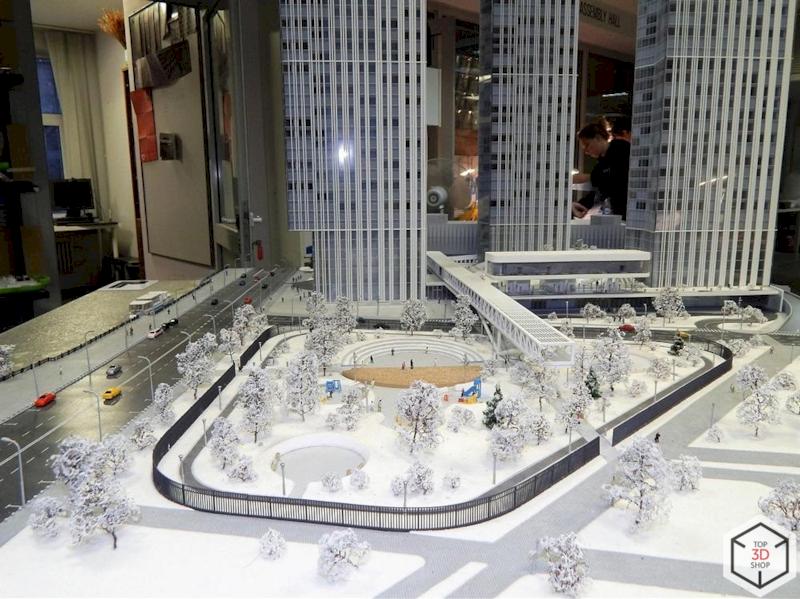

3D printing has transformed how this model studio works:
Workflows became faster and more predictable.
Accuracy and repeatability improved.
The range of possible scales and details expanded dramatically.
3D printers now handle much of the routine, repetitive work. This frees skilled specialists to focus on:
Creative tasks
Complex compositions
Final assembly and finishing
As a result, overall productivity and flexibility have grown, while the studio still keeps and uses the best parts of its traditional craft.
Buy large-format FDM and resin 3D printers for architectural and industrial model studios at Top3DShop — our specialists will help you select the right machines, materials, and configurations to support both high-volume production and fine-detail work in your projects.

Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment