
3D printing technologies have been around for some time, so most people are used to their integration into various areas of life. A 3D printed car part or a phone case is a matter of course, and even printing dental models already looks pretty commonplace. Yet, there are some unexpected applications of additive manufacturing that are just beginning their way into the market. One of them is 3D printed food, which is getting a lot of attention since cooking, or at least consuming food, is something everyone deals with in everyday life.
This is Top 3D Shop, and in this article, we are going to explore the exciting world of 3D printed food and look at the process of haute cuisine creation with the FELIX Food 3D printers.
Not so long ago, the idea of producing food on the push of a button could be found in sci-fi novels or movies. And like many other concepts, invented by fantasists, this one has found its implementation in the form of food 3D printing. Although the process in reality looks a bit more complicated than just pushing a button, the technology seems very promising and opens up numerous opportunities for the food industry, so experts predict its rapid growth. Essentially, food 3D printing is a material extrusion process, in which the role of material is played by edible ingredients that are extruded through a nozzle onto a build surface layer by layer. Just like with FDM printing, a 3D model of the future delicacy is converted into STL file format and sliced, generating a G-code file used for printing.

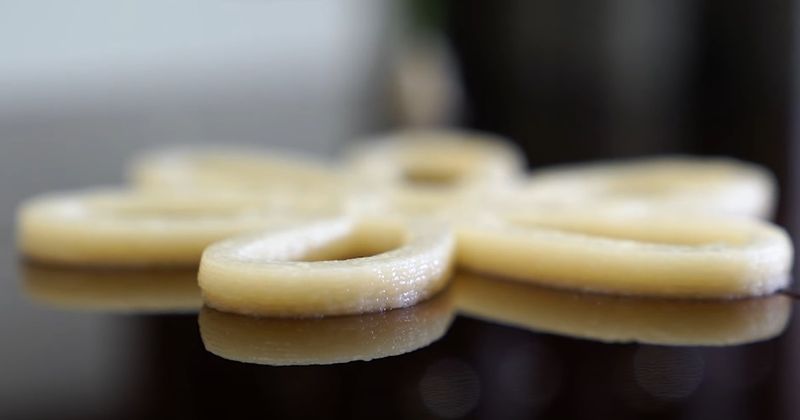
One of the first edible materials used for 3D printing was chocolate, as it has the perfect viscosity for extrusion and solidifies pretty fast, retaining the desired shape, which allows intricate designs to be created. Later on, the list of printable food was considerably expanded with fruit, vegetables, meat, cereals, cheese, dairy products, dough, and more. All ingredients should be in the form of a paste or puree and have the right viscosity to pass through the nozzle without clogging it and hold the desired shape when extruded. Additives, such as thickening or gelling agents can be used to improve printability. Another purpose of using additives is to personalize the final product and make it ideally suited for the needs of a person or group of people, such as children, the elderly, athletes, or people suffering from certain diseases. In such cases, adding precise amounts of minerals, vitamins, probiotics, or other elements to 3D printed food helps strictly keep to a specific diet.
Alongside design freedom and personalization, food 3D printing allows some processes to be automated with high repeatability and precision. Besides, using exact amounts of ingredients reduces food waste and makes for cost reduction of the final product.
Fascinating as it sounds, food 3D printing has its downsides, which, however, are likely to be overcome as the technology develops. One of them is a relatively low print speed, which is a limitation for industrial-scale applications. Another point that needs researching is material properties that can vary to a great extent due to natural origin. These problems can gradually be solved through extensive R&D work and investments in the sector growth.
The FELIXprinters company was established in 2011 and is headquartered in in IJsselstein, the Netherlands. The founders of the company, father and son Feliksdal, started with a ‘home factory’ and launched their first FDM 3D printer, the FELIX 1.0. After a year, they moved to a real office and since then the company has been developing and producing FDM printing solutions. In 2015, they announced their first 3D printer in the Professional series, the FELIX Pro 1. Today, FELIXprinters offer different models in Entry level, Professional, Industrial, and Pro HT lineups as well as consumables and accessories. Apart from that, having gained experience in designing FDM machines, the company launched the FELIX BIOprinter followed by the FELIX Food 3D printer series under the FELIX food brand. The manufacturer says that their food printers are targeted at the professional and industrial market, but consumers will also appreciate their reliability, ease of use, and customer service provided by the company.

The FELIX Food 3D printer is a compact open-frame machine that looks and operates similar to an FDM 3D printer, which uses edible paste-like materials instead of thermoplastic filaments. Unlike many food printers, that are limited to the use of a single material type, often chocolate, or to proprietary material cartridges, the FELIX Food 3D printer handles various pastes and purees that are loaded into disposable 100 ml syringes, providing endless opportunities for chefs and creative home cooks. The machine is easy to use and equipped with a number of features for reliable and convenient operation, such as a built-in camera, a heated print bed with auto calibration, or a selection of interchangeable nozzles with different diameters for greater versatility in material usage and product design. There are three modifications of the FELIX Food 3D printer, namely the Single, Twin, and Switch versions.
The Single head model is equipped with one nozzle and prints with a single material. The Twin version has two nozzles that are fixed at a certain distance from each other and print simultaneously, allowing you to build two identical models, thus doubling the production volume. And the Switch head machine also features two cartridges that can be filled with different materials to be combined in a single project. The smart mechanism allows swapping between the two nozzles in just seconds.
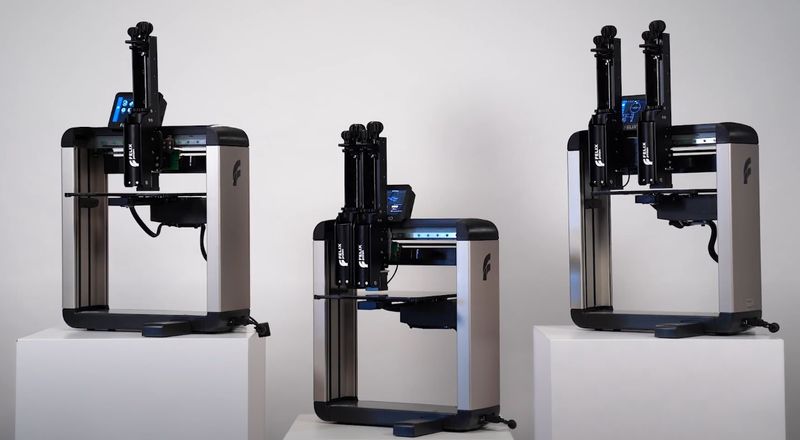

When using the Twin head machine, the print area is divided into two parts where identical models are printed on both of them, doubling the output, compared to a Single head version. The build volume and maximum material capacity for different models are shown in the table below.
| Single head | Twin head | Switch head | |
| Build volume | 270 x 195 x 170 mm (10.6 x 7.6 x 6.7 in) | 130 x 195 x 170 mm (5.1 x 7.6 x 6.7 in) x 2 | 260 x 195 x 170 mm (10.2 x 7.6 x 6.7 in) |
| Print volume capacity | 100 cm³ | 200 cm³ (2 x 100 cm³ syringes) | 200 cm³ (2 x 100 cm³ syringes) |
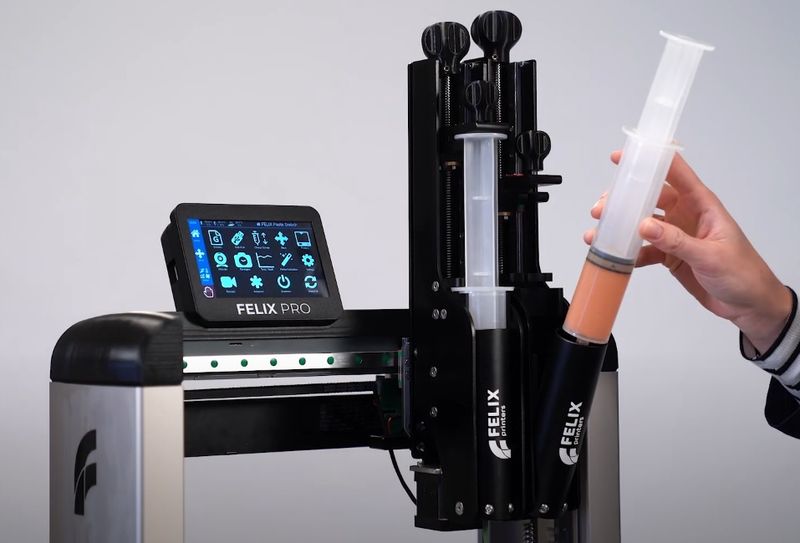
To start printing, one needs to fill the syringe with a chosen material and load it into the cartridge. Once you prime the syringe by rotating the knob to eliminate bubbles, your machine is ready to use. The FELIX Food 3D printer utilizes food-safe disposable 100 ml syringes with a Luer lock system. Available nozzle sizes vary from 1.2 to 3.5 mm, while the layer thickness ranges from 0.5 to 2 mm. The Twin and Switch machines allow it to load two syringes simultaneously, but the user can also choose printing with only one nozzle at a time. For materials that need heating for better extrusion, the manufacturer offers an optional heated syringe with a maximum temperature of 50 °C.

The printer comes with a flexible removable build plate made of 316L stainless steel that can heat up to 100 °C, providing the optimal conditions for the material being printed. Once the job is over, the printed food can be easily removed. Or you can place the build plate into the oven in case your models need baking, like cookies, pastries, or meringues. The user can choose to print on a silicone mat, that is also oven-safe. Both surfaces are easily cleaned and meet the hygienic cooking standards.

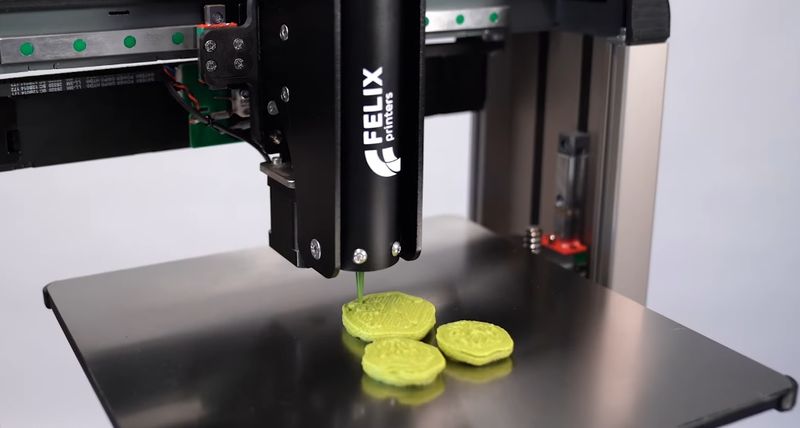
As mentioned, the FELIX Food 3D printers can process numerous materials in the form of a homogeneous paste. For successful printing, the ingredients should have the right viscosity and smooth texture to ensure consistent extrusion and a precise shape of the finished dish. Generally, any edible substance that can be turned into a paste suits for 3D printing. Ingredients can be combined and enriched with special additives, which provides an unlimited number of recipes and opportunities for food personalization. Some popular materials include fruit and vegetable purees, chocolate, butter, sugars, soya, avocado, mashed potatoes, seaweeds, dough, and egg white, just to name a few.

All the three models feature a 5" capacitive touchscreen with an embedded octa-core processor. An intuitive user interface allows for convenient operation with all the main menu items brought to the home screen.
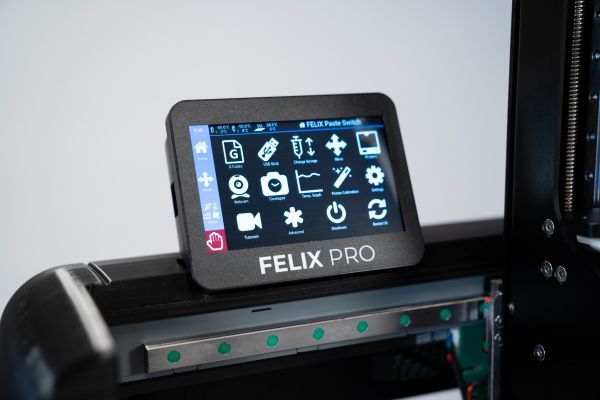

There are various connectivity options, including Wi-Fi, LAN, and USB. When using a USB stick for uploading the G-code, you can print directly from it or save the file into the printer’s memory. The machine features 16 GB of RAM. To control the printer via LAN or Wi-Fi network, go to the Settings menu and choose WLAN option or plug in the Ethernet cable to the slot on the side of the touchscreen. The FELIX Food 3D printer is compatible with Repetier-Server, so you can control the printer remotely via web-interface. The built-in camera allows for real-time monitoring of the print process, and you can record a timelapse video of your print.
The recommended software to use with the FELIX Food 3D printer is Simplify3D. It is crucially important to use the slicing profiles provided by the manufacturer for stable operation and reliable print results. So, once you install the Simplify3D software, be sure to import the slice profiles from the supplied SD card or the FELIXprinters website. Further on you will need to choose your printer’s model from Single, Twin, Switch Left (Right) only, and Switch Dual options.
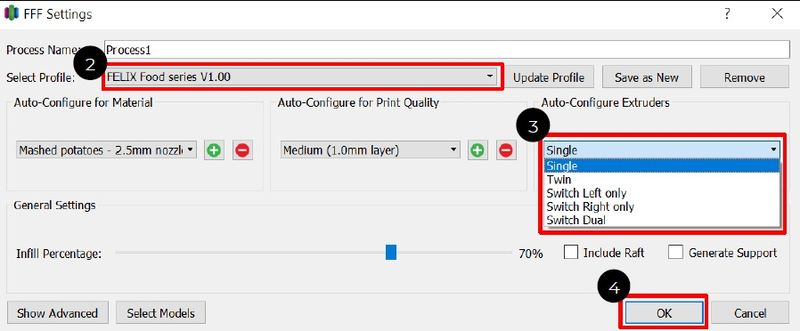
After you import an STL file, you need to adjust print settings, such as material type and nozzle diameter, layer height, and percentage of infill, before slicing the model. A raft can be added to your print if needed. As for support structures, they are not generally used in food 3D printing. Apart from selecting one of the predefined material types, it is possible to create your own material profile, defining the parameters of extrusion, such as extrusion multiplier, extrusion width, retraction distance, and others, and temperature settings. If you adjust such parameters as material price and density, you will be able to see the estimated model cost in the preview window.
The FELIX Food 3D printer can find its use in gourmet restaurants, where it will help automate cooking routines and attract customers with amazing culinary masterpieces. It can also be used in hospitals to prepare special food for patients who suffer from swallowing problems. In food labs, the FELIX Food 3D printer will become a research tool for testing various ingredient combinations. Cooking enthusiasts can also greatly benefit from having a food printer on their kitchen counter, as it boosts creativity and gives familiar food a completely new look, feel, and taste.
The video below shows the process of chocolate printing.
Children are more willing to eat broccoli if it is served in such an unusual way.
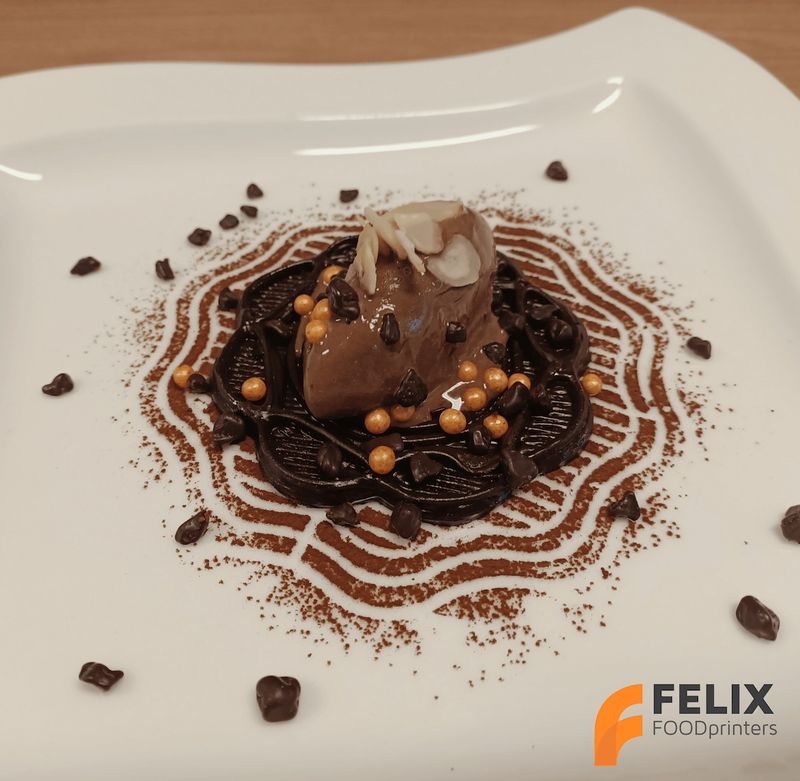
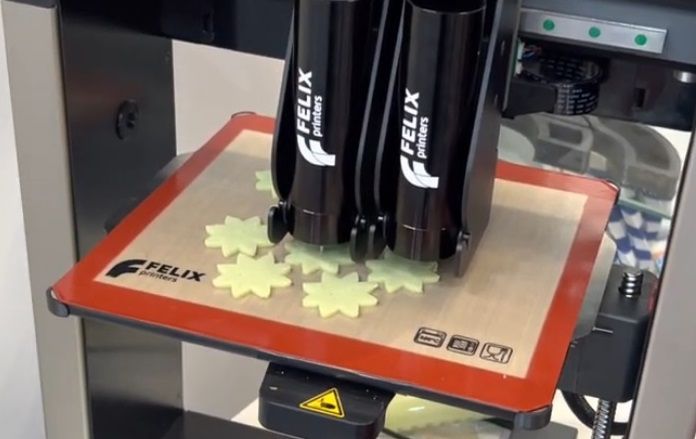
Below are some more examples of FELIX Food 3D printer’s creations.
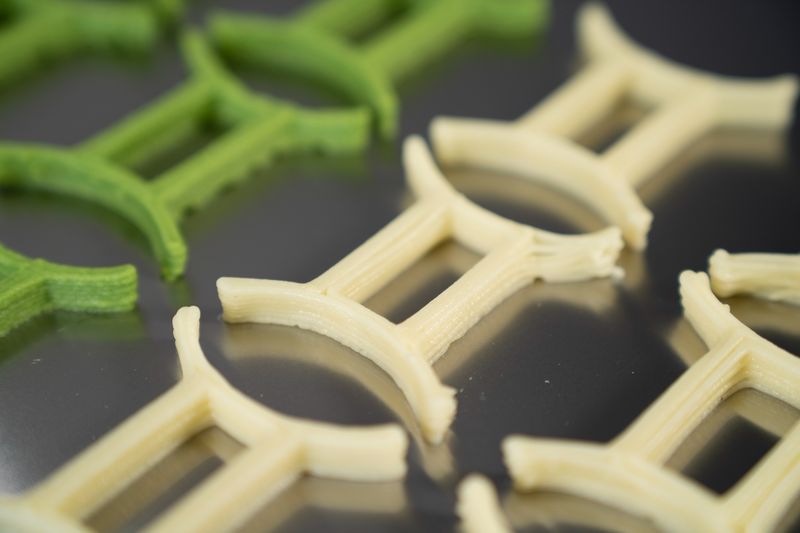
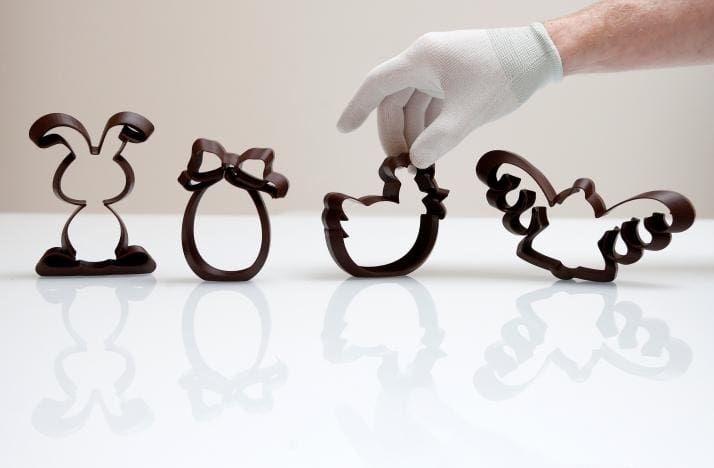


Food 3D printing has a lot of potential benefits, from creating unique shapes that could be difficult, if not impossible to create by hand, to the opportunity to use uncommon ingredients and prepare personalized food that meet any specific requirements. The FELIX Food 3D printers are a good example of versatility, quality, and convenience of use in this rapidly evolving market.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment