
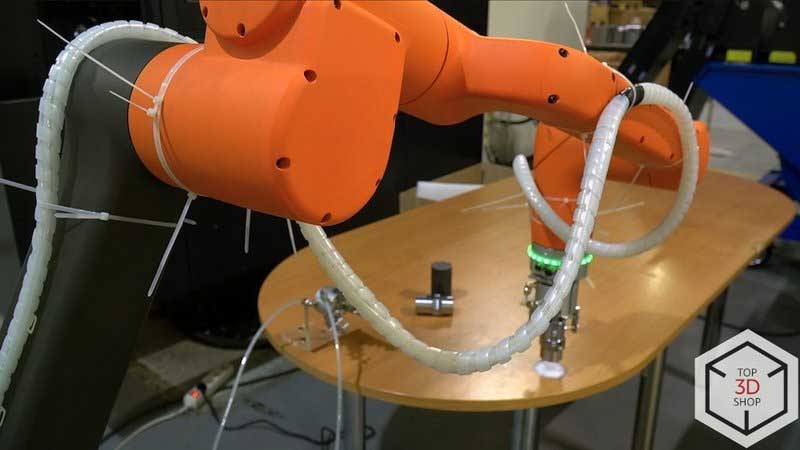
We helped a hydraulics manufacturer integrate a Hanwha HCR-12 collaborative robot with a Mazak QT-Compact 100 MYL CNC turning center to increase output in their turning area without adding extra operators or floor space.
This hydraulics manufacturer started in 2005 as a supplier of high-quality Italian hydraulic equipment for industrial machinery and special vehicles.
Key milestones and capabilities:
2017 – launched in-house production, introduced a quality management system.
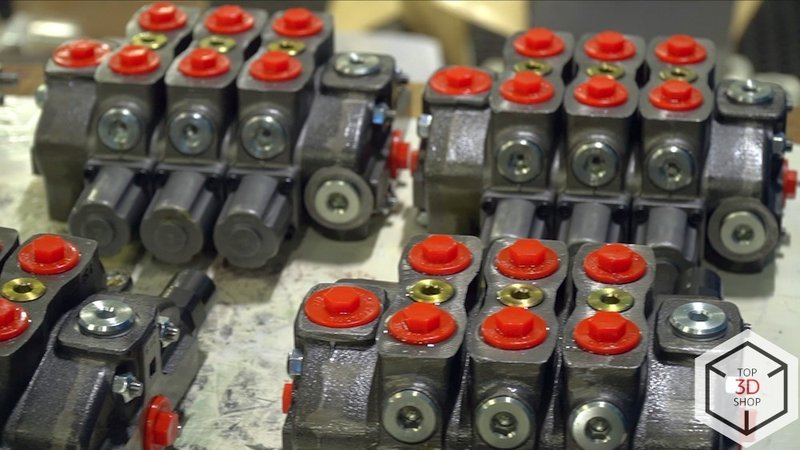
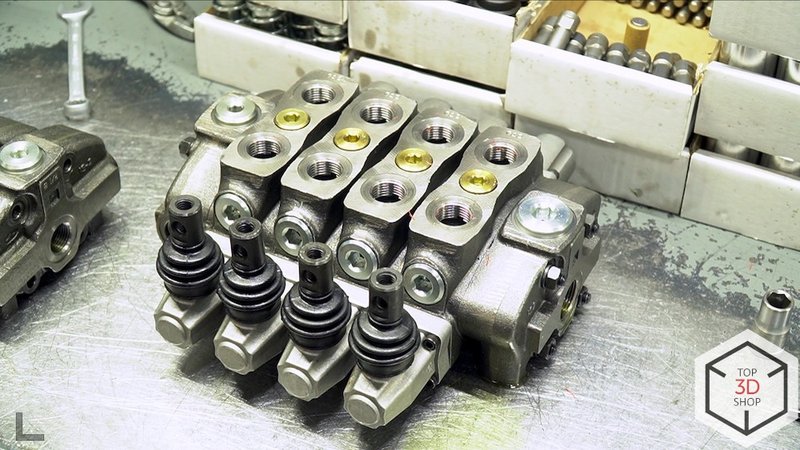
Established assembly of:
hydraulic distributors
valves and valve boxes
complete hydraulic systems


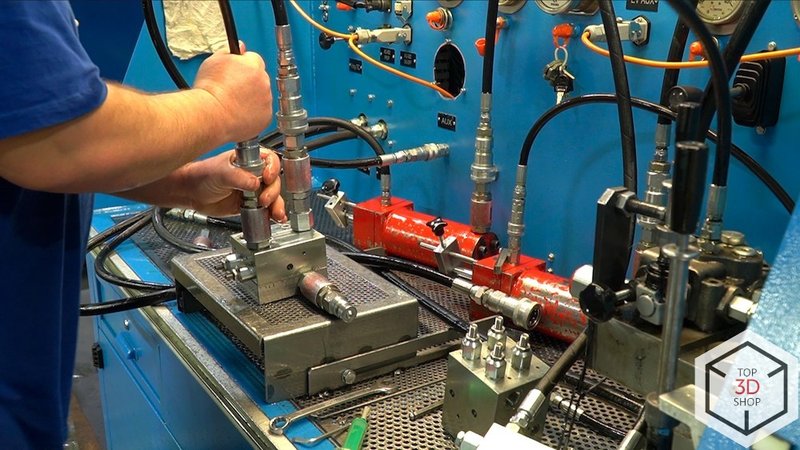
All products go through final testing on a self-made test bench.

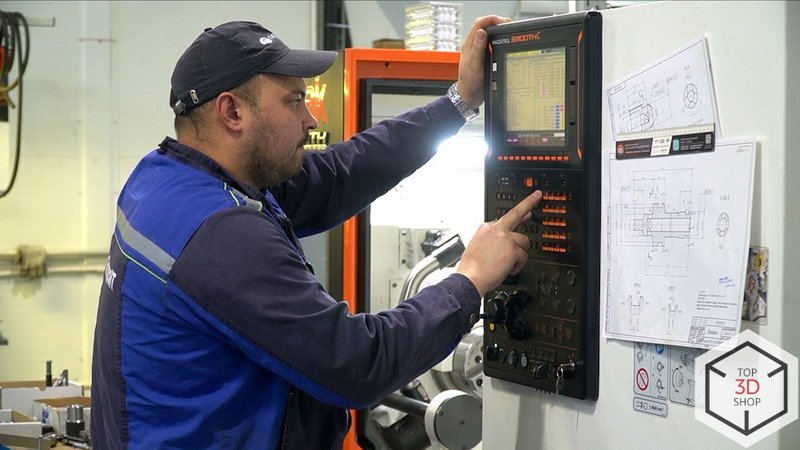
Specializes in volumetric hydraulic drives and mechatronic systems.
Supplies components for:
road and agricultural machinery
special vehicles
marine vessels
mobile lifting platforms
industrial, mining, and oil & gas equipment
Staff: 50+ employees.
Production: modern CNC machining centers, test benches, and auxiliary equipment.


Provides technical support, warranty, and post-warranty service.
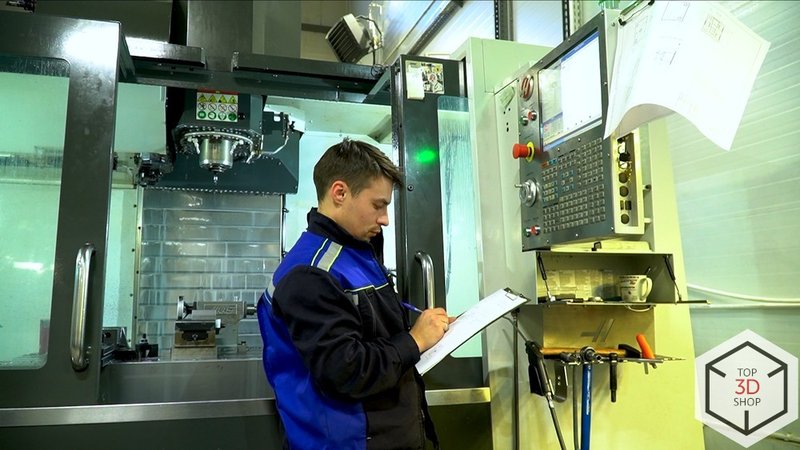

By 2020, demand grew enough that lead times started to increase. Management set two main goals:
Increase labor productivity
Expand production volume in the turning area
Process analysis showed a bottleneck in turning operations, especially on the Mazak QT-Compact 100 MYL:
Short part programs didn’t always give operators enough time to service the machine in an optimal mode.
Operators sometimes left the machine unattended to handle other tasks.
The company decided to automate part handling at the turning center to stabilize cycle times and reduce idle time.
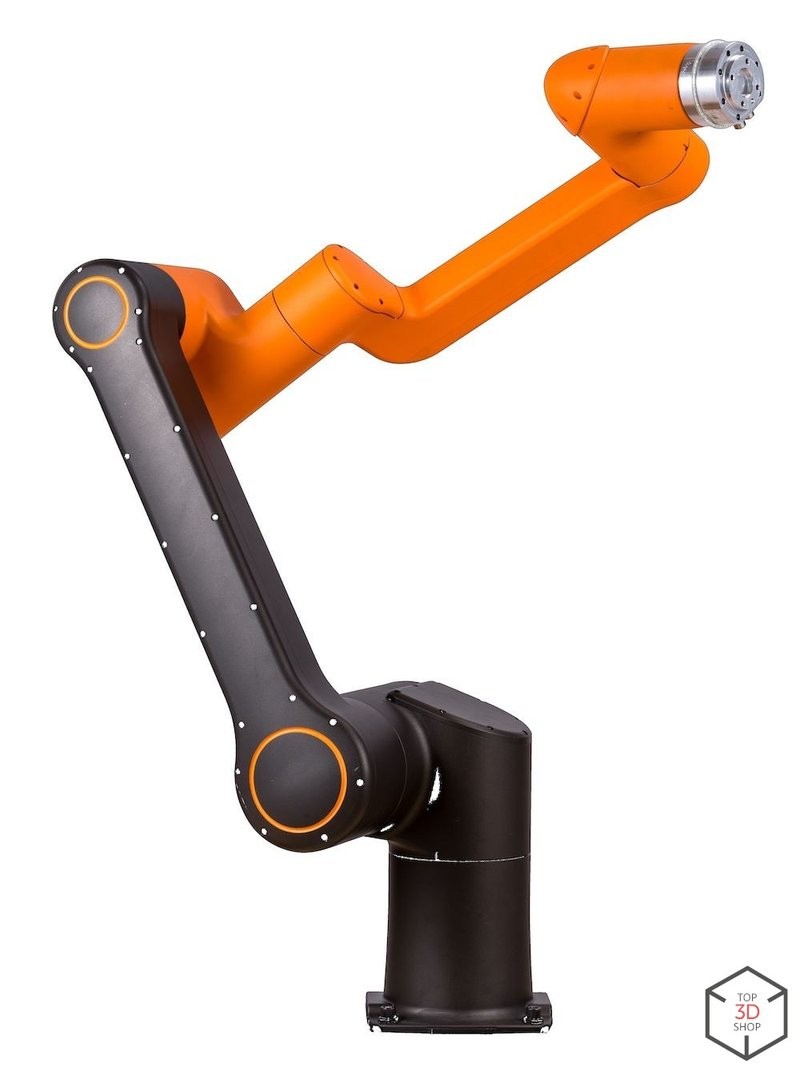


The HCR series includes HCR-3, HCR-5, and HCR-12; the number indicates payload in kg. The HCR-12 offers the highest payload and longest reach (1300 mm), which makes it suitable for:
Machine tending
Welding
Loading/unloading
Palletizing
Joint speeds and torques are limited for safe human–robot collaboration.
Built-in sensors detect sudden obstacles and stop the robot via servo drives.
Supports virtual restraints to limit motion zones.
Uses Rodi software with a touch screen and intuitive interface, so even operators without deep programming skills can set up and adjust tasks.
Watch a video about Hanwha collaborative robots.
When the company looked at ways to optimize production, they considered several automation options and robot brands.

They chose collaborative robots (cobots) instead of large industrial robots because cobots:
Occupy minimal floor space
Can work close to operators without large safety fences
Fit easily into existing layouts and process chains
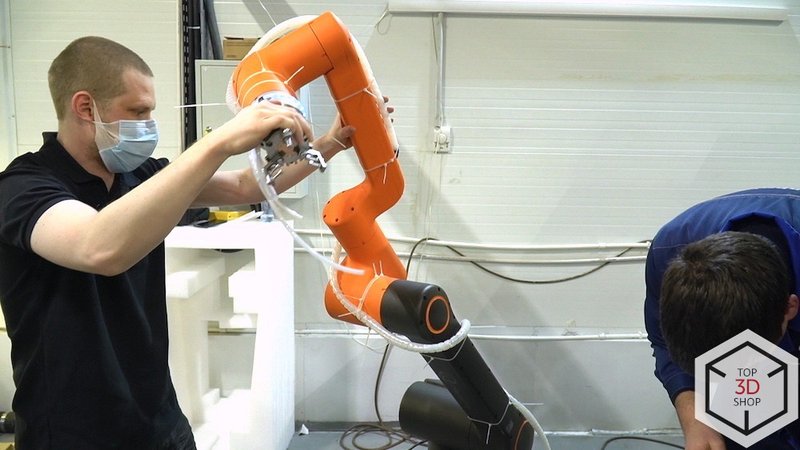

Technical experts at the plant evaluated demo units from multiple manufacturers for compatibility with the Mazak turning center and for ease of integration.
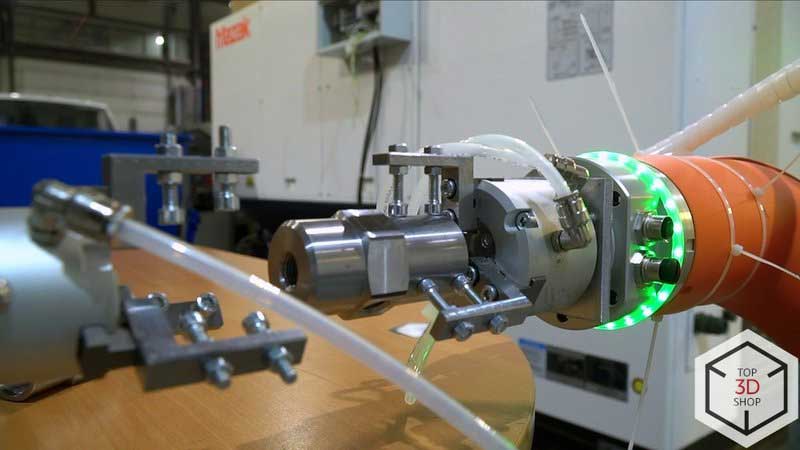

The Hanwha HCR-12 supplied by Top3DShop stood out as:
The most convenient and reliable option
Easy to integrate into the existing process chain
Equipped with user-friendly software that plant technicians could master quickly
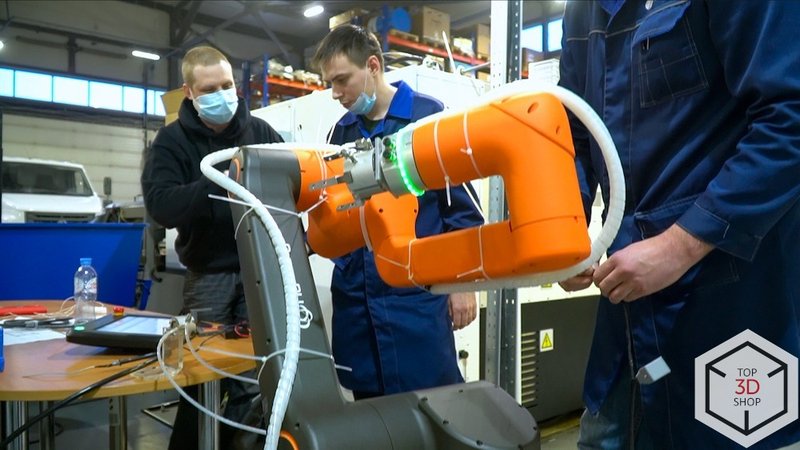

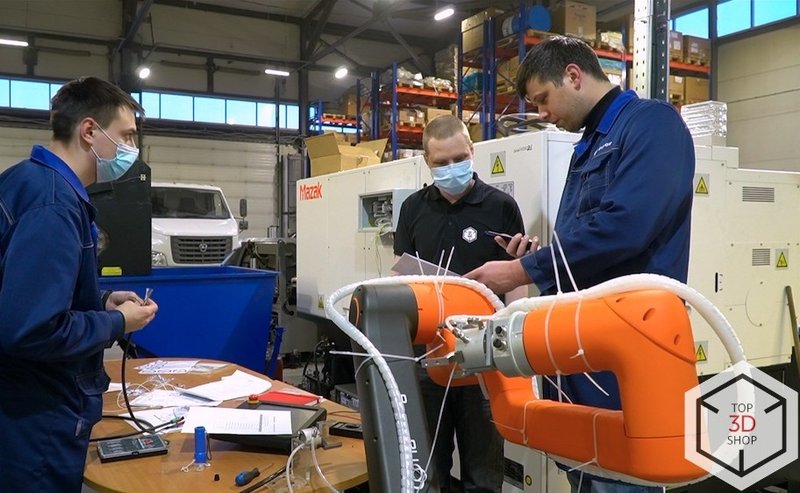
Top3DShop engineers:
Installed and commissioned the robot
Trained the company’s technicians to program and operate the cobot
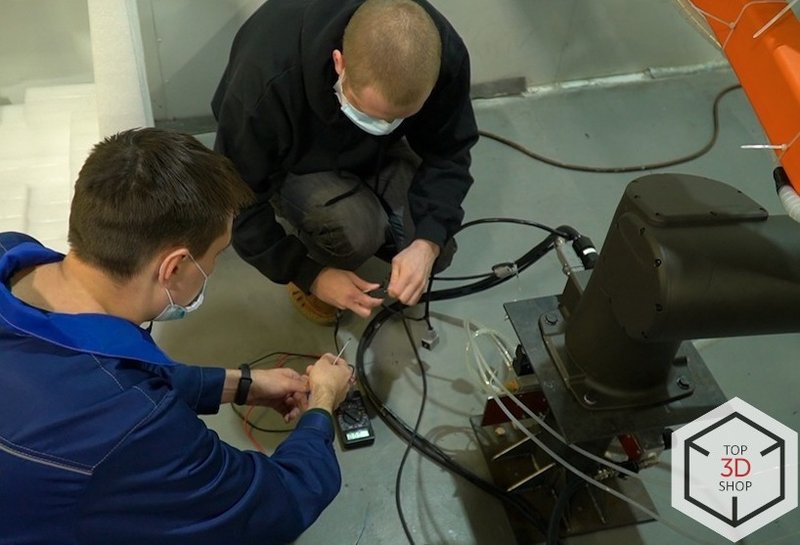
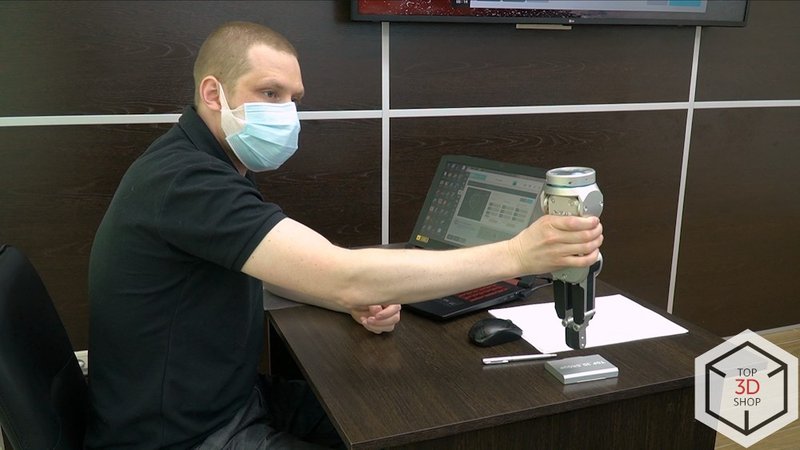


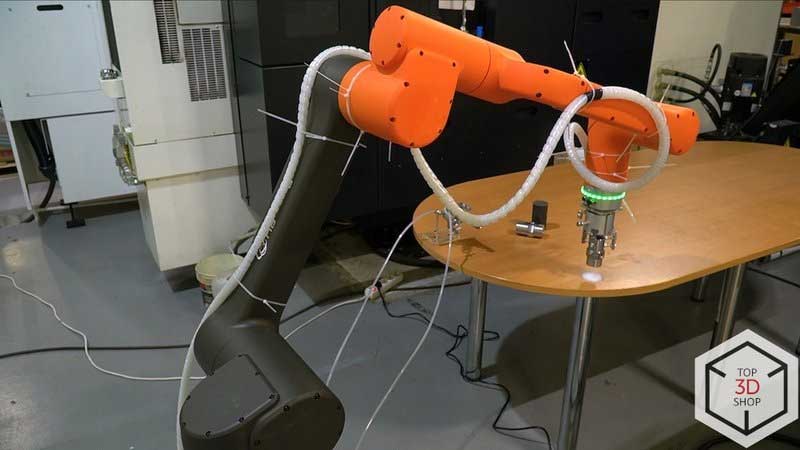
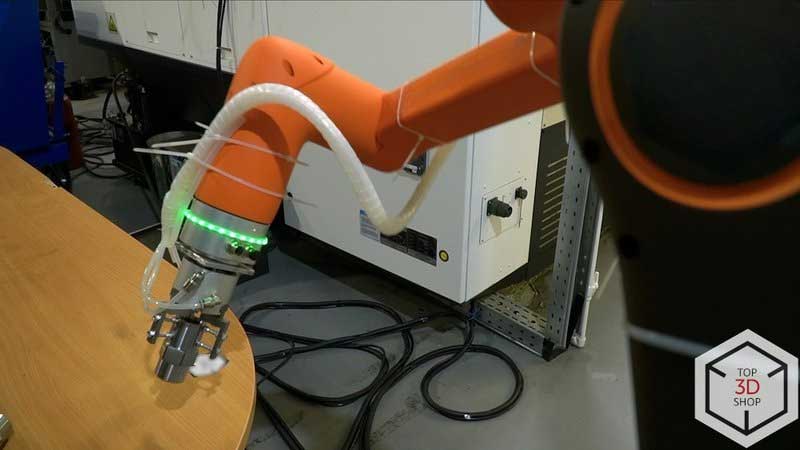
The plant integrated the HCR-12 into the turning area to automate loading and unloading at the Mazak QT-Compact 100 MYL.
Key effects and workflow changes:
The cobot now handles routine machine tending operations.
The operator can monitor two or more CNC machines at once, instead of being tied to a single turning center.
The system reduces idle time caused by short programs and inconsistent manual servicing.
Management emphasizes that they introduced cobots to assist skilled staff, not replace them. Operators keep control of the process while the robot takes over repetitive handling tasks.



The company’s preliminary calculations show:
Payback period for the Hanwha HCR-12: no more than 3 years
This aligns with average robot payback times in many industries.
If you want to estimate the payback of introducing robots in your own production, contact us for a detailed calculation.
This project became the company’s first major step in process automation.

Future plans, if the current payback projections hold:
Expand the fleet of collaborative robots
Use cobots not only on turning centers but also to service milling machines
The successful integration of the Hanwha HCR-12 with the Mazak turning center gives the plant a scalable model for further robotization of its machining operations.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment