
Today we will talk about the advantages of manufacturing automation and major robot suppliers as well as the main types of industrial robots and examples of their use in various industries.
One of the reasons for the rapidly increasing automation in production is that robotics is becoming more affordable. Over the past decade, the price for robots has fallen by almost 30%, and in the next 10 years it will probably be reduced by another 20–22%. Robotics not only continues to develop within large enterprises, but it is also steadily implemented into medium and small businesses.
Practically all leading robot manufacturers are now engaged in producing robotic manipulators and collaborative robots designed for SMEs. Interestingly, large companies often buy them alongside traditional industrial robots as well.
Changying Precision Technology, McDonald’s, Vanguard Plastics Corp, and FANUC Robotics have conducted a series of case studies that showed:
The paper under the title ‘Robotics application in flexible manufacturing systems: prospects and challenges in a developing country’ by S.K. Bello provides the calculation of the ultimate benefits of robot deployment:
|
Financial flows |
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Year 5 |
|
Initial investment |
-66500 |
||||
|
Tax credit (10%) |
6650 |
||||
|
Initial cost |
-14100 |
||||
|
Tax credit |
7050 |
||||
|
Depreciation of equipment |
13300 |
13300 |
13300 |
13300 |
|
|
Taxes |
-6650 |
-6650 |
-6650 |
-6650 |
-6650 |
|
Wages and benefits of a replaced worker |
33000 |
36300 |
39930 |
43923 |
48315 |
|
Taxes |
-16500 |
-18150 |
-19965 |
-21962 |
-24158 |
|
Productivity gains |
40000 |
44000 |
48400 |
53240 |
58564 |
|
Tax |
-20000 |
-22000 |
-24200 |
-26620 |
-29282 |
|
Maintenance cost |
-2500 |
-2750 |
-3025 |
-3328 |
-3660 |
|
Tax credit |
1250 |
1375 |
1513 |
1664 |
1830 |
|
Power consumption |
-2400 |
-2640 |
-2904 |
-3194 |
-3514 |
|
Tax credit |
1200 |
1320 |
1452 |
1597 |
1757 |
|
Annual savings |
-39500 |
44105 |
47851 |
51970 |
56502 |
Currently, there are many robotics companies around the world, so let’s take a look at some of them.
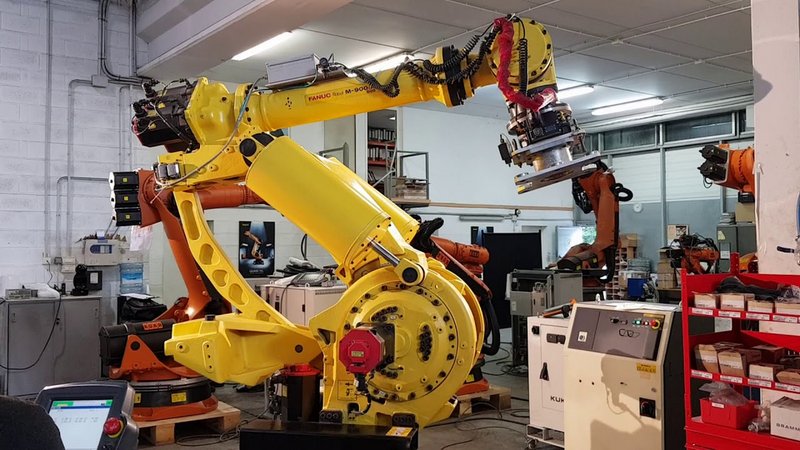

FANUC M900ia-600
This Japanese company specializes in industrial automation. FANUC is the largest manufacturer of industrial robots in the world, judging by the number of robotic manipulators used worldwide.
In 2018, the company celebrated the production of its 500,000th robot. FANUC is constantly expanding the product range with new technologies and solutions. They produce delta robots as well as various machines for painting, welding, palletizing, etc.
Credit: fanuc.eu
Flexlink, a company that builds automated conveyor systems, uses a FANUC M-1iA delta robot in combination with an LR Mate 200iD articulating robot on a new line for pharmaceutical blister packs. The first robot aligns the position of products and evaluates their quality. If it is satisfactory, the product is placed on an intermediate belt in front of the pick station. The LR Mate 200iD then packs the products. The complex reaches the speed of 60 pieces per minute.
The video below shows a wide range of industrial automation solutions with FANUC robots: machine maintenance, palletizing, removal of excess material from the part, spot welding, etc.

Hanwha HCR-5 cobot
Hanwha is one of the largest conglomerates in South Korea. Robot manufacture is only a small part of its production.
Hanwa’s collaborative robot is the first of its kind in South Korea. The company’s cobots are a good solution for small companies due to their easy control compared to conventional industrial machines, while the benefits of their introduction remain the same. Additionally, they are cheaper to maintain.
The application range of collaborative robots continues to expand from industrial to commercial uses. For example, the HYRobotics HCR-5 in the following photo serves chocolates.
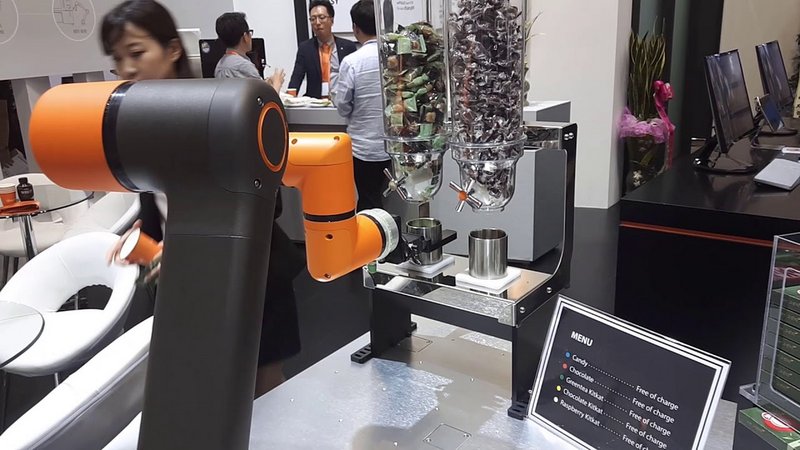

The operation of the barista robot is demonstrated in the video below.
And here, the same robot is unloading machined parts from a Doosan CNC machine.

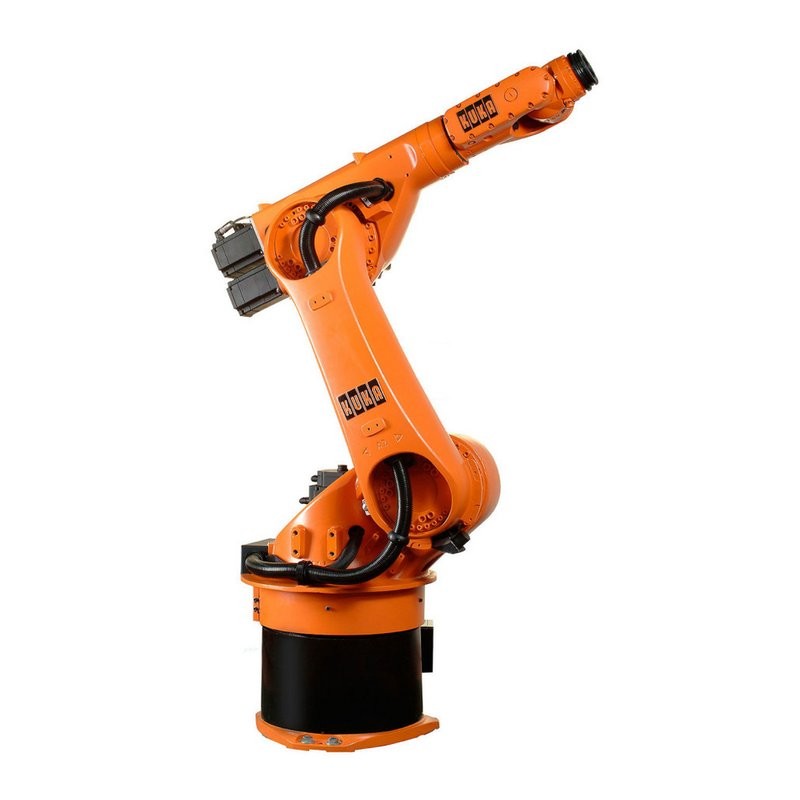
KUKA offers industrial robots for various purposes, with different payloads and reach. They are used in many industries for welding, loading, palletizing, packaging, machining, assembly, and other operations.
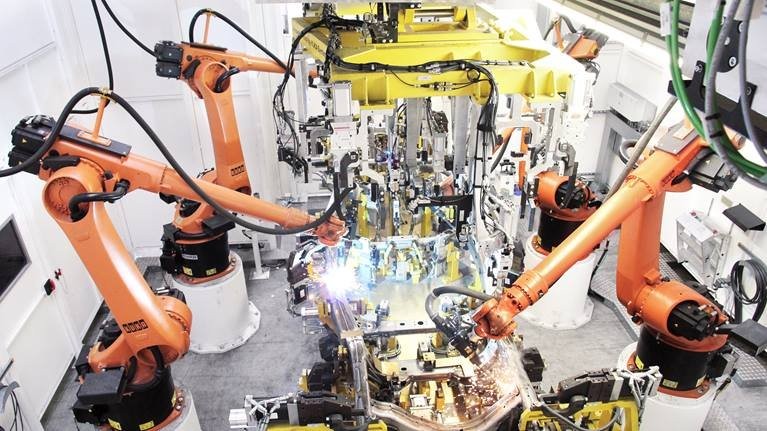

Robot-assisted arc welding at the Gestamp plant
Gestamp specialists produce ladder frames for Volkswagen vehicles. The Gestamp plant in Bielefeld uses a fully automatic arc welding system from KUKA Systems to ensure the highest quality, process reliability, and high output with minimum labor requirements.
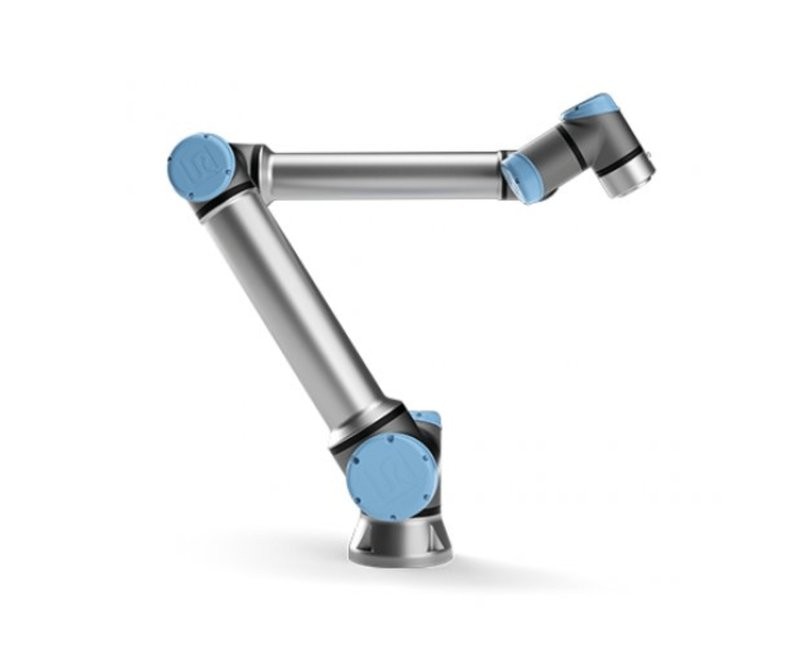

Universal Robots is a Danish manufacturer of small and flexible industrial collaborative robots.
The company has introduced many innovations, including the use of smaller and inexpensive robots that do not need to be separated from human workers. In 2008, the first UR5 robot appeared. The second, UR10, was launched in 2012. Finally, the UR3 was announced in 2015.
Universal’s fantastic success is probably due in part to the fact that its robot was the first cobot as it is seen now: an autonomous unit working in collaboration with humans. But more importantly, it boasts a superior design emulated by other robot manufacturers.

The UR robot at the Continental plant cooperating with a CNC machine
In 2016, Continental purchased several UR10 robots to automate the loading and unloading of circuit boards and component mounting. The transition time from one processing mode to another was cut in half compared to manual labor.
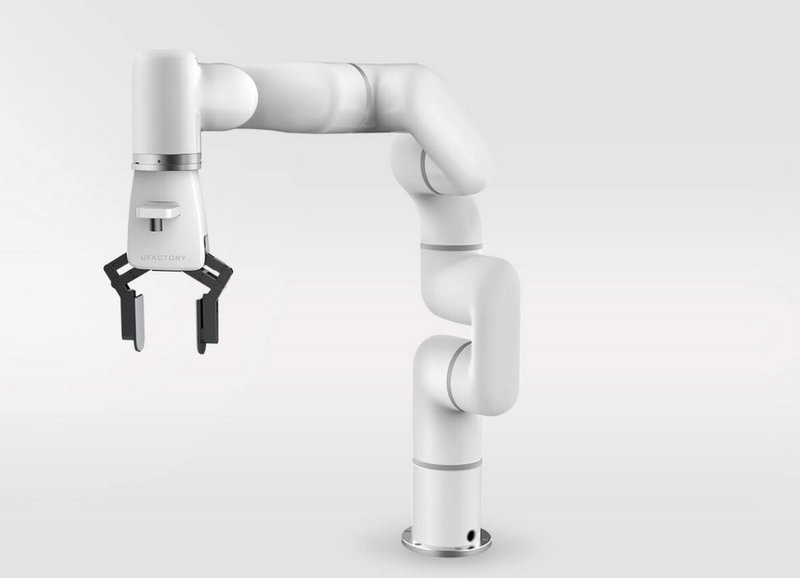

UFactory xArm
UFactory is a Chinese startup. It has released cost-effective and intuitive desktop robotic manipulators for education and small business, such as the uArm Swift Pro and xArm System.
The xArm comes in three versions: the 5-axes xArm 5 Lite with a payload capacity of up to 2 kg, the more flexible 6-axes xArm 6 (5 kg), and the 7-axes xArm 7, which can handle loads up to 3.5 kg.
The video shows how the uArm Swift Pro can be used for 3D printing.
Find out more about the spheres of the xArm applications from the video.
In April 2019, the International Federation of Robotics provided the preliminary robot adoption rates by industry worldwide:
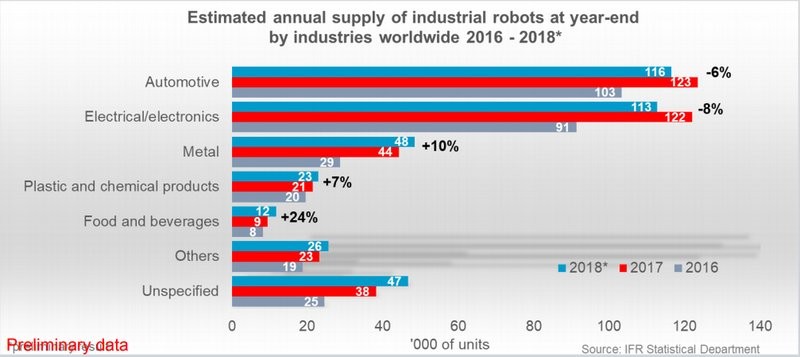
As can be seen from the chart, the automotive sector is in the lead. Together with the electrical/electronics, they cover about 60% of the market. Although the sales numbers have slightly decreased compared to 2017, which is not surprising: robotization in these industries began a long time ago and was carried out at a rapid pace. Thus, the outlook for the future is very positive.
The implementation of industrial robots in metal, chemical, food, and other industries is further increasing.
Industrial robots can be used wherever accuracy and speed are required, where monotonous or dangerous for human operations and aggressive environments are implied.
Here are just a few examples of the robotics applications in various industries.
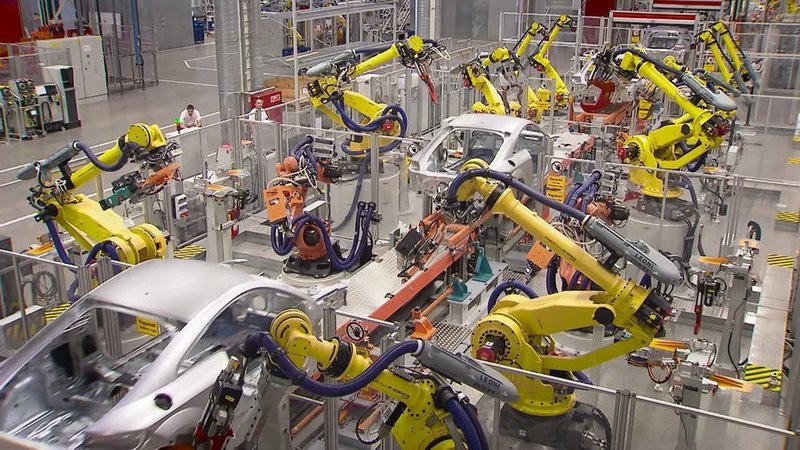

Audi assembly line
Credit: fanuc.eu
Audi is one of the companies with the largest turnover and export in Hungary. It produces cars with the help of FANUC industrial robots.
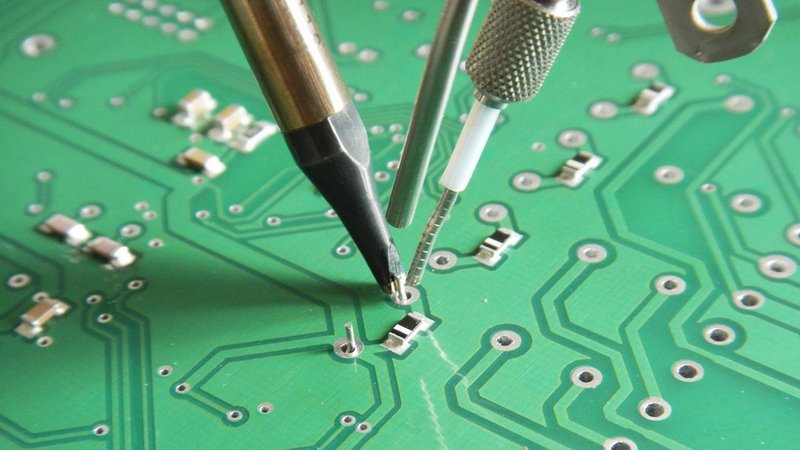

The KR 6 R900 robot soldering the board
Credit: kuka.com
ALNEA Sp. z.o.o. specializes in the production of customized test equipment. The KUKA KR 6 R900 robot is used for selective soldering of printed circuit boards. As a result, ALNEA has achieved the highest precision soldering and reduced the production process time by half.
The video shows the robotic assembly of CPU and memory modules on a PCB.
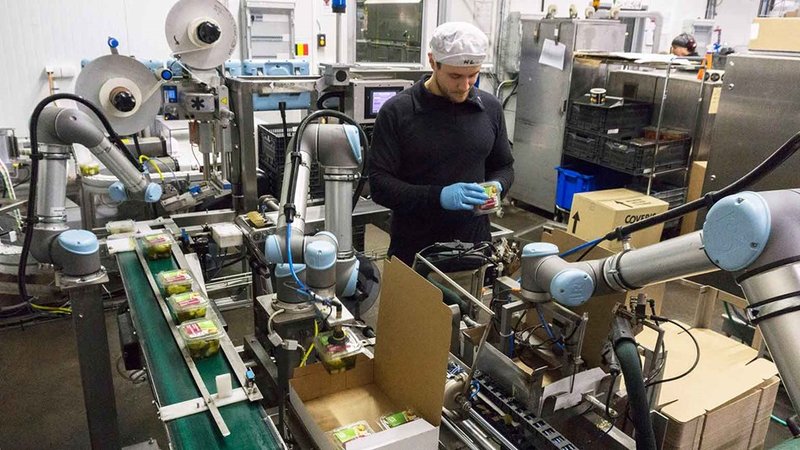

UR cobots packing food
Credit: universal-robots.com
Atria Scandinavia is a Swedish producer of vegetarian and gourmet foods. Every day a mass of products is packed, labeled, and stacked. The whole process is optimized: the UR10 collaborative robots prepare more than 200 items per hour on each production line for shipment. The payback period amounted to one year.
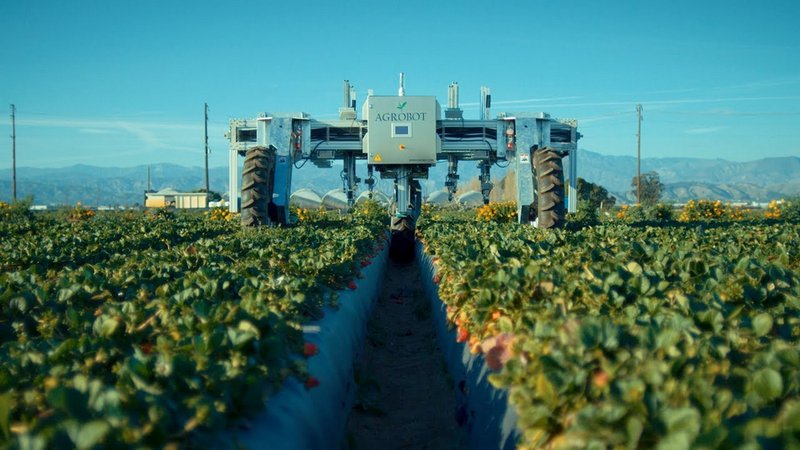

Agrobot SW6010
Credit: agrobot.com
Although, at first glance, it may look like a tractor, the robot in the photo is a strawberry picker. The machine is equipped with sensors and manipulators to detect ripe strawberries and pick them.
Robots are classified according to a variety of criteria: by the operations performed, payload, control system, construction, and technical features. Robotics is evolving so quickly that there are almost no standards in this sphere. Often, models can be classified in more than one category.
In this article, we will make a conditional division into the main types.
These are robots performing certain operations, whose functionality is structurally defined. These include welding, assembly, medical robots, etc.
The task of these machines is to stack products in pallets according to a programmed pattern, perform loading and unloading.
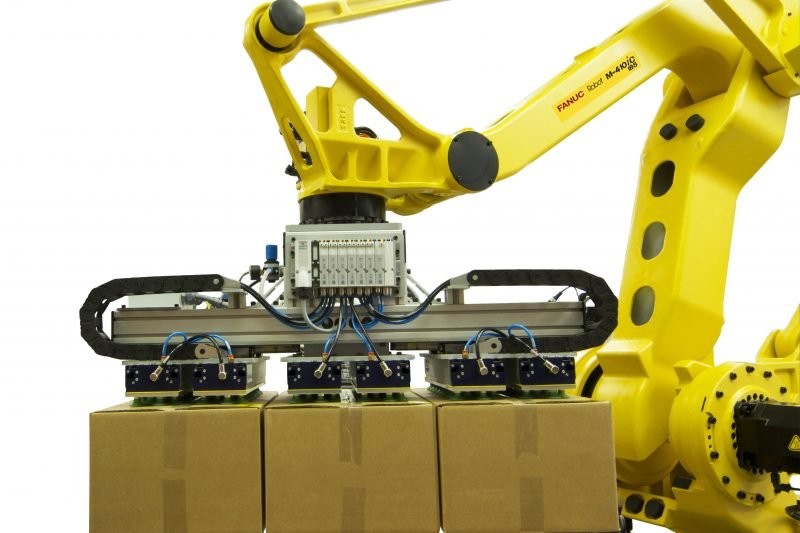

Credit: fanucamerica.com
The FANUC M410 series robots are designed for medium to heavy loads (up to 700 kg).

Credit: fanucamerica.com
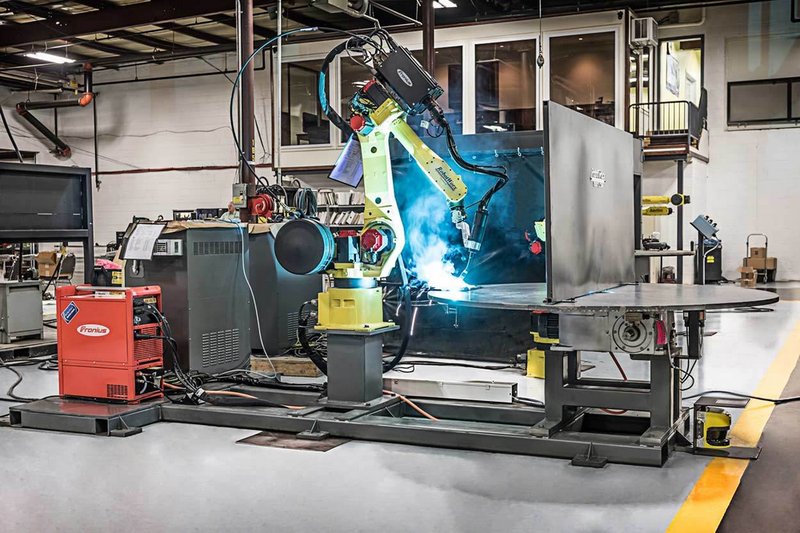
The FANUC Arc Mate series robots can perform arc welding, laser welding, and soldering.
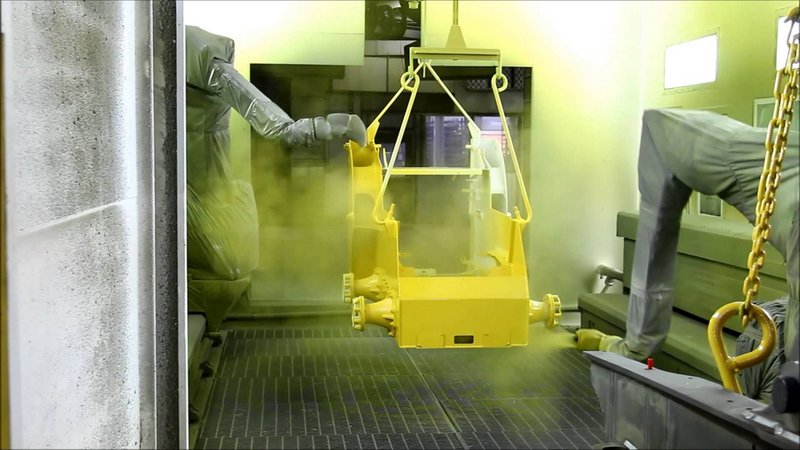

The operation process of two FANUC Paint robots
Credit: nordrobotics.lt
Painting robots equipped with spraying devices are successfully used in different industries ranging from consumer goods to heavy engineering.

Credit: sealing-system.dk
Conventional industrial robots are servo-driven robotic arms with a large number of degrees of freedom. Their movements are usually limited by their size and construction peculiarities. These robots can rotate around the base and extend the tool at different angles, making movements with a complex trajectory.
This type is perfect for many operations; the application is limited only by the availability of tools that can be integrated into the design.
These include grippers or pneumatic suction cups used for moving objects, loading and palletizing; welding or 3D printing machines, paint sprayers, and more.
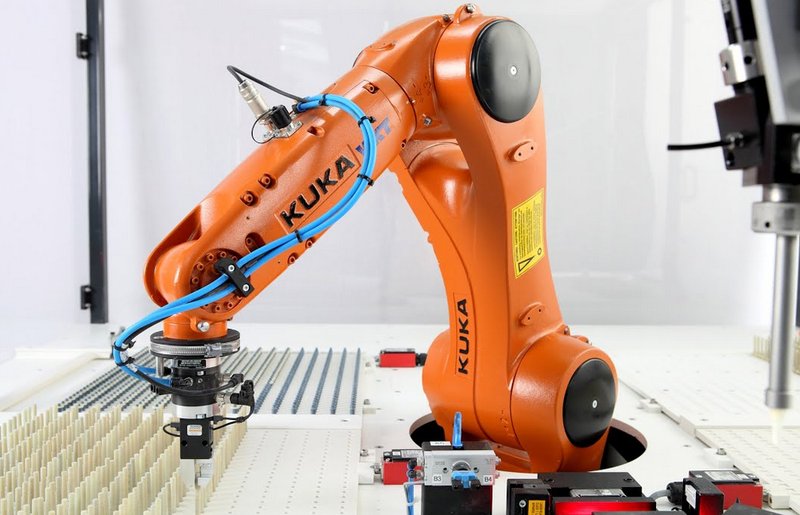

The KUKA KR AGILUS robot makes threaded bolts and validates the result
Credit: kuka.com
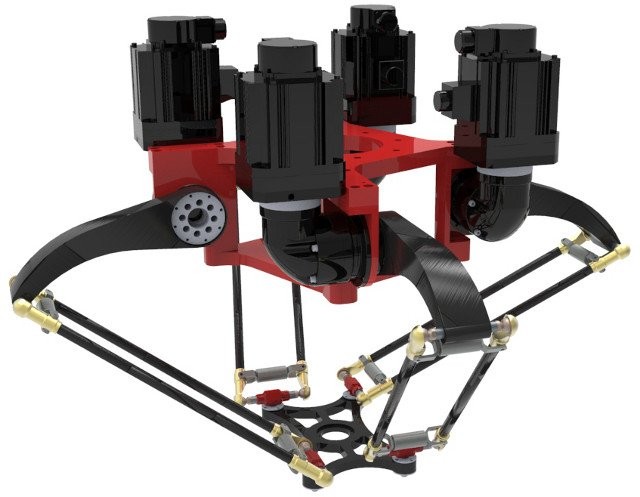

Credit: coro.etsmtl.ca
Robots based on delta mechanics often perform packing and assembly functions on conveyors. Machines of this type are engineered to make precise and quick movements. This configuration is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and electronic industries. Delta robots arrange electronic components on printed circuit boards for subsequent soldering, fill packages with small parts, and perform other operations that require not only accuracy, but also speed.

FANUC M-2iAs delta robots pack Belgian waffles
Credit: fanuc.eu
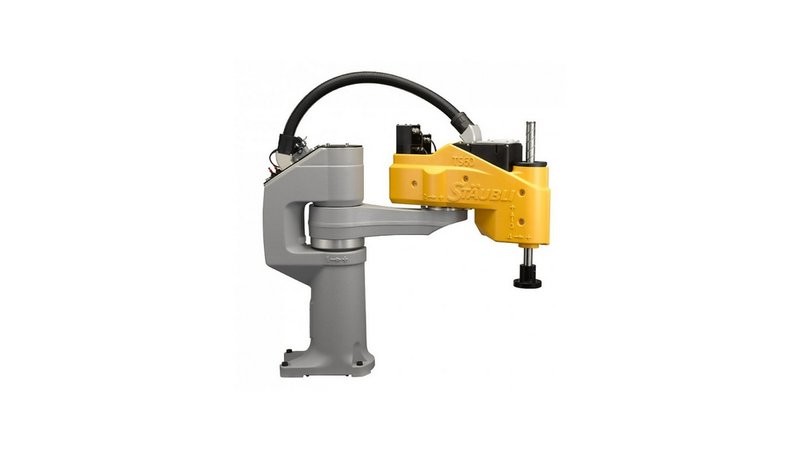

Credit: hannovermesse.de
Based on the SCARA kinematic scheme, these robots have excellent accuracy and repeatability. They outperform conventional manipulators and delta robots, but generally have fewer degrees of freedom and a much smaller operating range due to design characteristics.
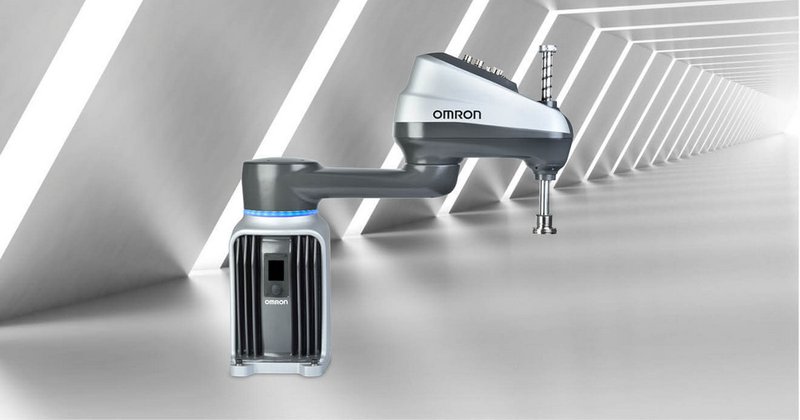

OMRON i4 SCARA
Credit: fa.omron.co.jp
SCARA robots are used where accuracy is needed and the process is carried out in small access areas. For example, they are great for parts picking, quality control, handling components, etc.
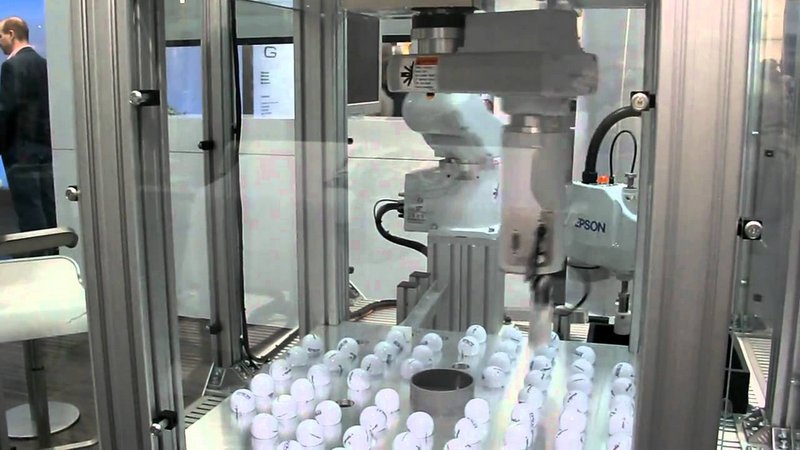

In the video, the Epson SCARA robot is really fast at sorting golf balls.
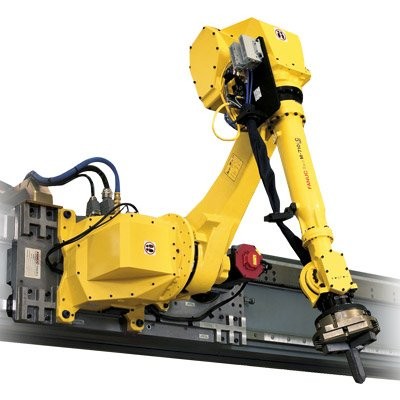

Credit: fanuc.eu
Robots can serve several machines at once. Some models are top-mounted on rails, which is convenient when the production area is limited. Thus, robots of this type can move from one machine to another. It is possible to equip them with different devices, depending on the needs of production.

The UR robot works with a CNC lathe machine
Credit: CNC Programmer
They are applied for loading material into CNC machines, unloading finished parts, and machine maintenance (lubrication, replacement of cutting tools or print heads, and more).

Credit: cnc-machine-tools.com
The video demonstrates an industrial robot serving a CNC machine.
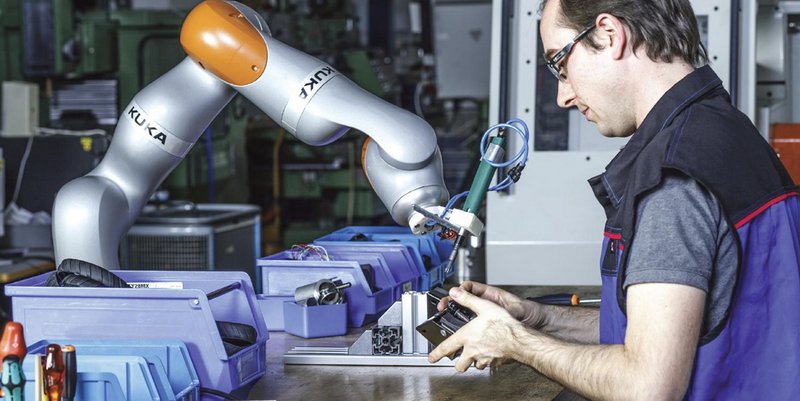

Credit: robots.com
Collaborative robots or cobots work in close proximity to and with humans. Their feedback system, based on various sensors and special algorithms, makes it possible to avoid collisions of moving robot parts with cooperators and extraneous objects not provided for by the control program.
Originally, cobots were called compact assistant robots (see photo), but now they can include all robots capable of close cooperation with humans in a completely safe manner.
Today, robotics is being used more extensively than ever before, with manufacturers increasingly implementing automation to stay competitive.
The application of robots in production is cost-effective for any company regardless of its size as it usually increases productivity as well as product quality and improves working conditions for human personnel.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment