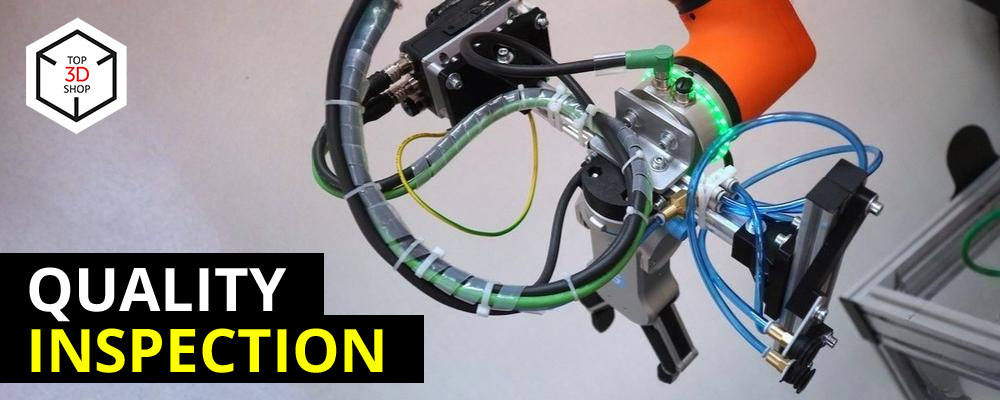
In late 2020 and early 2021, we integrated a comprehensive robotic solution for personnel training using the latest Fanuc, Hanwha, Omron, and Yaskawa industrial and collaborative robots.
The project aimed to create a full-scale model of a modern digital production line for an IT company.
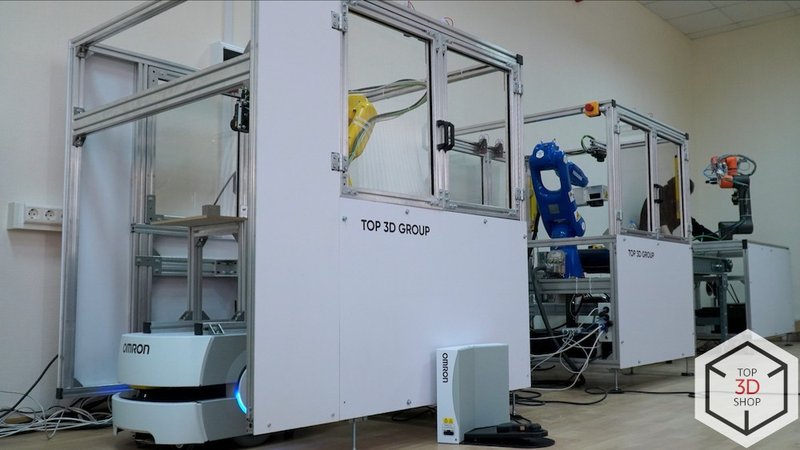

Project Overview
Top3DShop integrated industrial, collaborative, and mobile robots with all related equipment and software. We supplied every component, handled mechanical assembly, configured the software, commissioned the line, and trained the customer’s staff.
The customer will use this robotic complex to train personnel to maintain modern hardware and software. The project also gives them a real platform to test and scale their production automation concepts.
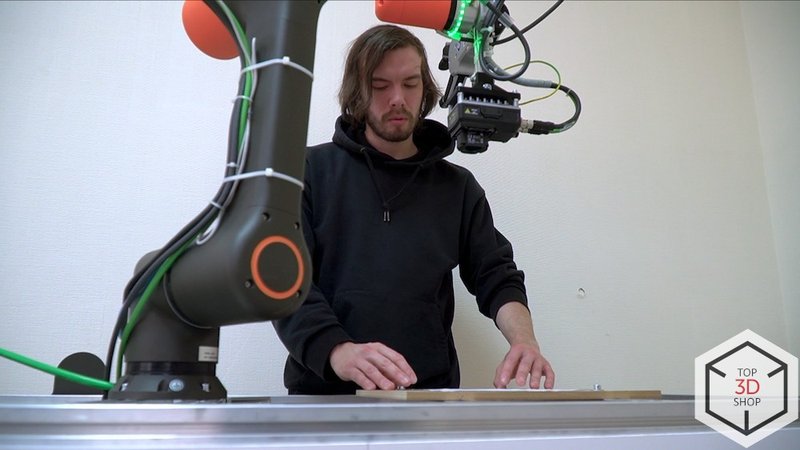
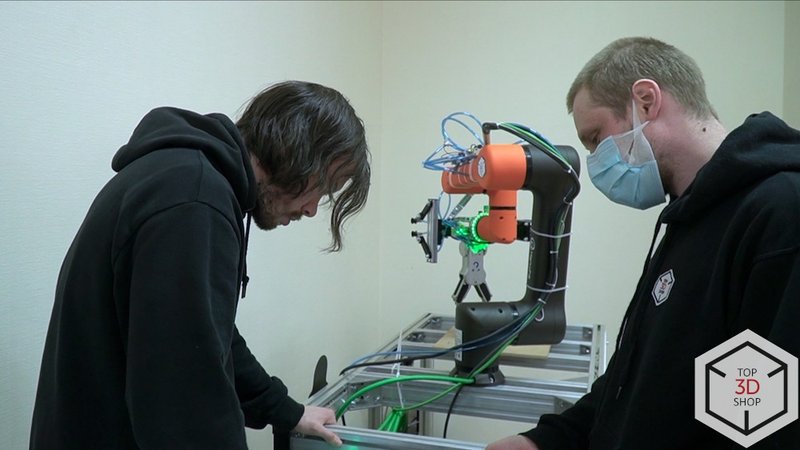
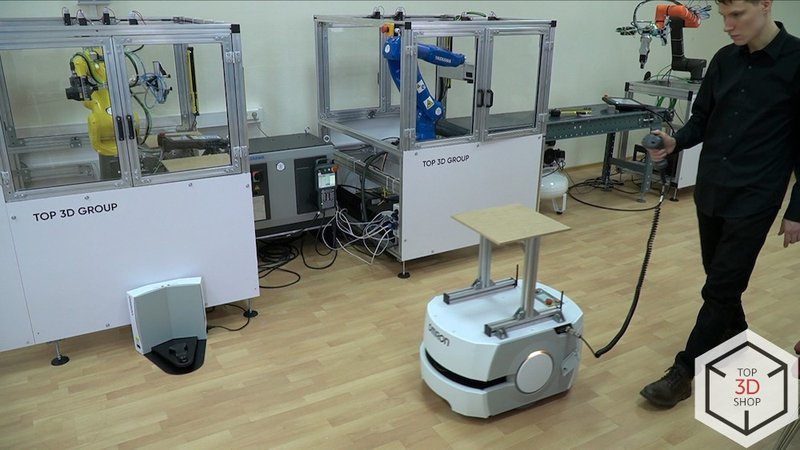




Equipment and system structure
Main equipment set
The training simulator includes:
-
Two industrial robots: Fanuc LR Mate 200iD and Yaskawa GP7
-
One collaborative robot: Hanwha HCR-5
-
One mobile platform: Omron LD-60
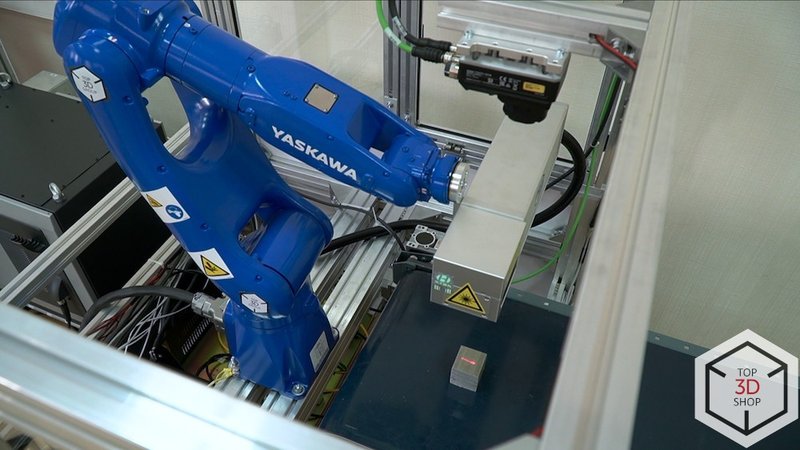

We also delivered:
-
Siemens SIMATIC S7-1500 controller
-
Omron FHV7 vision systems
-
OnRobot and SMC grippers
-
LSF-20 laser marker
-
Omron F3SG-R safety light curtains
-
Conveyor system
-
Silent compressor
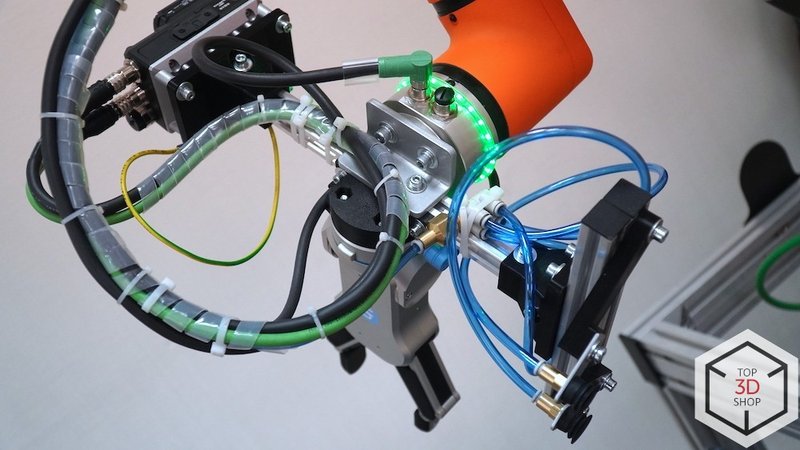
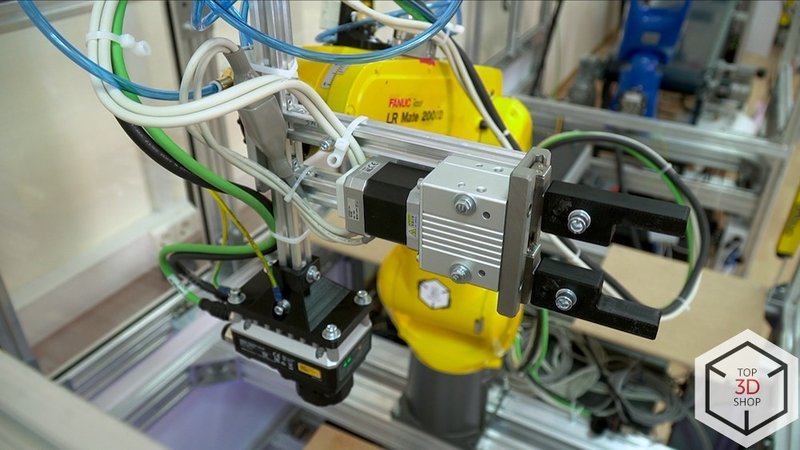
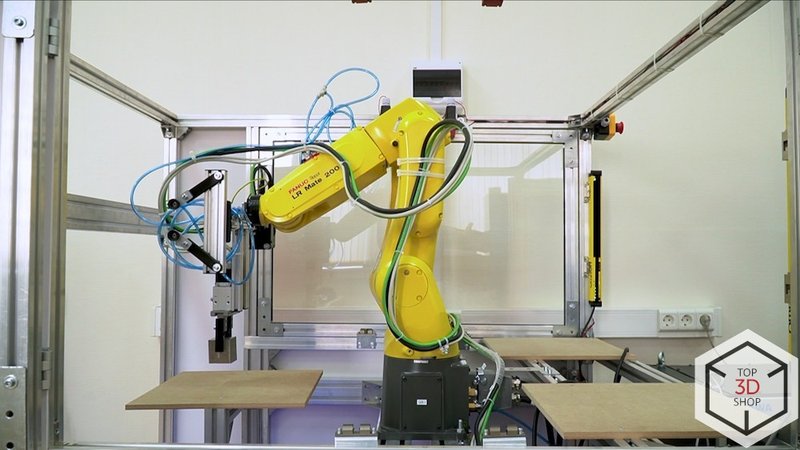
Fanuc LR Mate 200iD Robot Arm
Fanuc, a leading Japanese industrial automation manufacturer, focuses on CNC systems, laser equipment, industrial robots, and machine tools.
The LR Mate series consists of compact 6-axis robots that work in many industries — from food production to metalworking — and can operate in harsh or sterile environments.
Key specifications for the LR Mate 200iD:
-
Weight: 25 kg
-
Reach: 717 mm
-
Payload: up to 7 kg
It fits tight spaces and handles tasks like assembly, machine tending, and part sorting.
For this project, we equipped the LR Mate 200iD with:
-
An Omron vision system
-
Two SMC grippers:

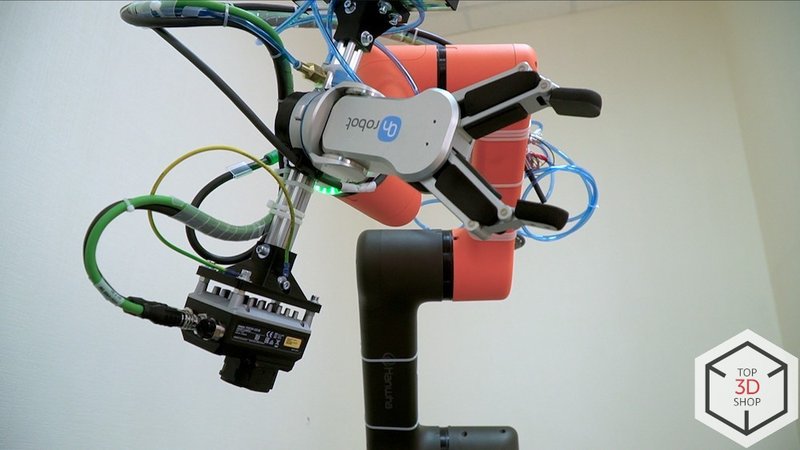
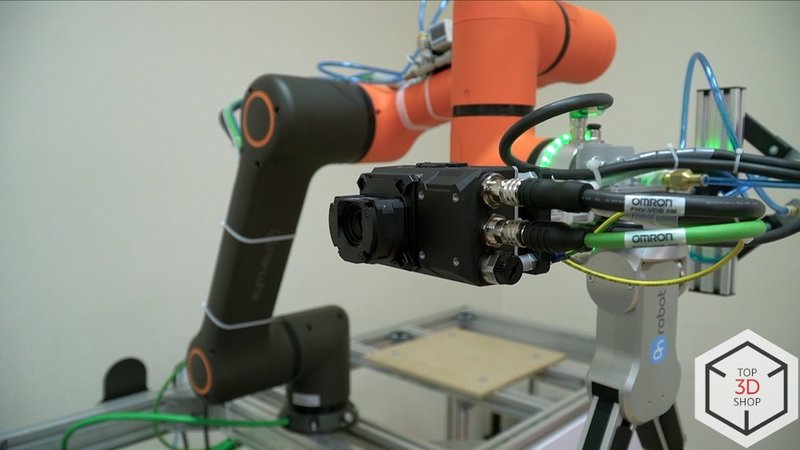
Hanwha HCR-5 Robot Arm

Hanwha Techwin — formerly part of Samsung and acquired by Hanwha in 2015 — has quickly grown in the collaborative robot market.
Its first cobot, the HCR-5, launched in 2017. The current Hanwha cobot lineup includes:
The model number corresponds to maximum payload in kg.
Key specifications of the HCR-5:
-
Reach: 915 mm
-
Payload: 5 kg
-
Offers a strong price-to-capability balance
-
Is the most popular model in the line
-
Holds a Class 2 cleanroom certification, making it suitable for electronics manufacturing
For this project, we equipped the HCR-5 with:
-
An Omron vision system
-
OnRobot RG6 gripper
-
SMC vacuum gripper
This setup lets the cobot handle multiple part types and gripping scenarios.
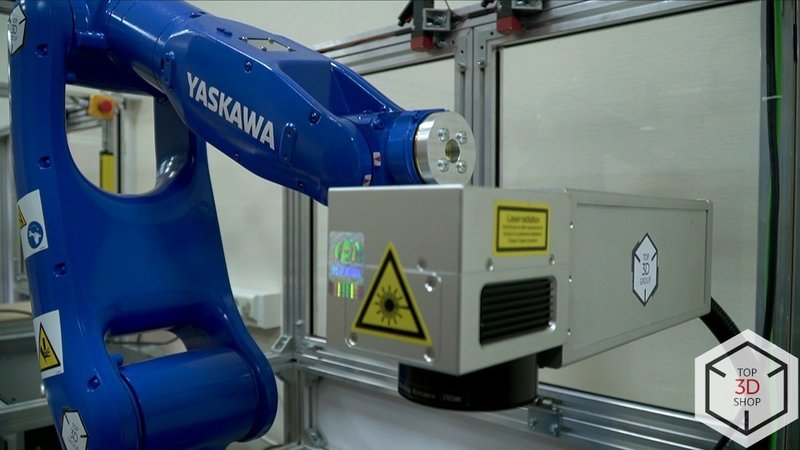
Yaskawa GP7 Robot Arm
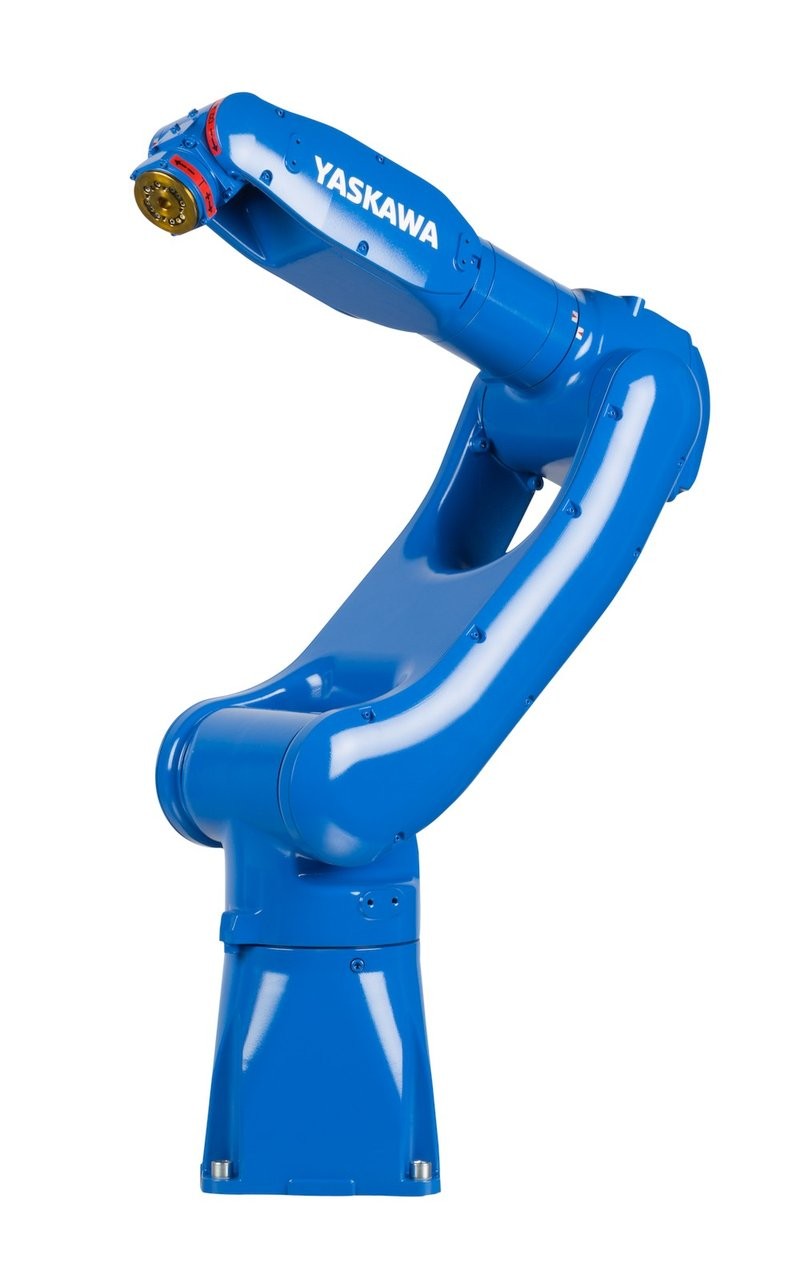

Yaskawa Electric Corporation has more than 400,000 industrial and collaborative robots in operation worldwide. Its product range includes over 150 robot models (articulated, delta, SCARA) and full sets of process equipment and safety devices.
The GP Series offers high-performance 6-axis robots optimized for:
-
Fast assembly
-
Packaging
-
Material handling
They provide high speed, precision, and flexibility in compact workspaces.
Key Specifications of GP7:
-
Payload: up to 7 kg
-
Compact footprint
-
High speed and power
-
Advanced motion control
In this project, the GP7 handles precise positioning and laser marking operations in limited space.
Omron LD-60 Autonomous Mobile Robot
The Omron LD-60 is a fully autonomous mobile robot (AMR) equipped with sensors and onboard software that allow it to navigate between predefined points without an operator.
Key capabilities:
-
Uses lidar, lasers, and SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
-
Plans routes and avoids obstacles dynamically
-
Outperforms traditional guided vehicles, which only detect obstacles but can’t reroute around them
In the line, the LD-60 transports workpieces between cells independently.

Production process
The robotic complex processes metal workpieces, engraves them with a laser, checks engraving quality, and sorts each part as “normal” or “defective”.
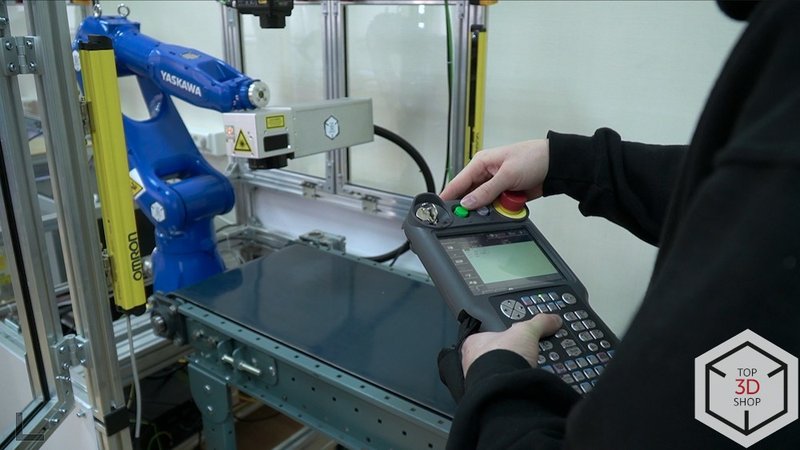
The operator starts the system from a central control panel that displays all components and their current status.
Step 1 – loading parts onto the conveyor
The Hanwha HCR-5, guided by its vision system and using either the OnRobot RG6 gripper or an SMC vacuum gripper, picks up a workpiece from the input box. It places the workpiece onto the conveyor and sends a signal to the main controller (CPU) to move the part into the engraving zone.
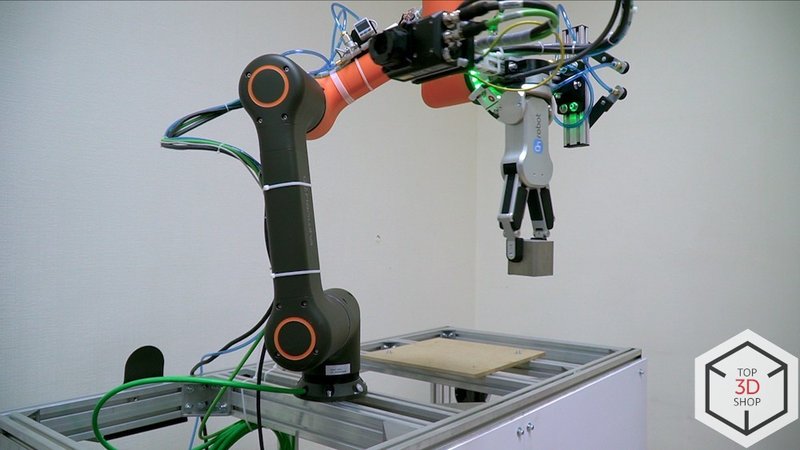

Step 2 – laser engraving
In the second cell, the Omron vision system identifies the workpiece type and orientation.
The Yaskawa GP7:
After engraving, the conveyor returns the workpiece to the Hanwha cobot’s working area.

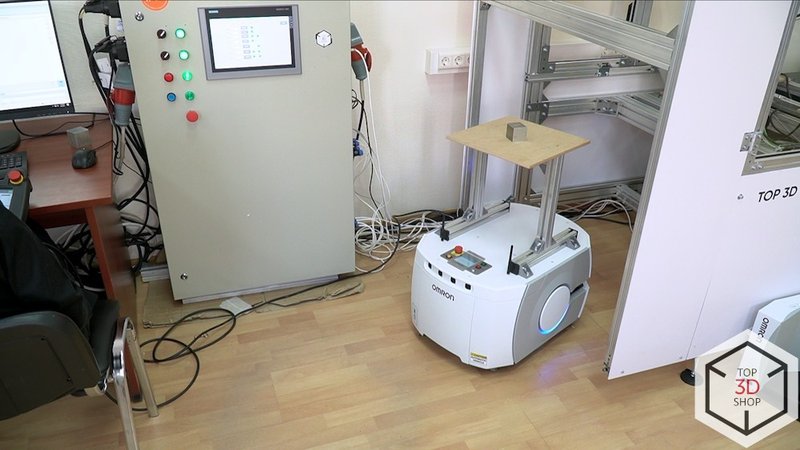
Step 3 – transport to the inspection area
The Hanwha HCR-5 then:
-
Picks up the engraved workpiece
-
Places it onto the Omron LD-60 mobile platform
-
Sends a signal that the part is ready for transport
The LD-60 autonomously drives the workpiece to the quality inspection cell.
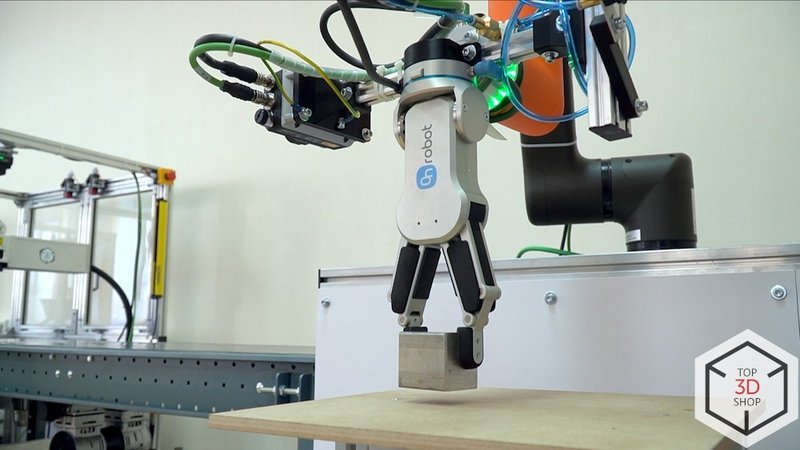


Step 4 – quality control and sorting
The Fanuc LR Mate 200iD uses its Omron vision system to inspect the engraving:
- It recognizes the workpiece type
- Evaluates engraving quality based on defined criteria
Depending on the type and result, the robot:
- Selects either the SMC 2-finger electric gripper or the SMC vacuum gripper
- Places the part into either the “normal” or “defective” zone
The system repeats this cycle until it empties the workpiece box or the operator stops the central control program.

Results and Lessons
Top3DShop engineers solved multiple integration challenges while synchronizing equipment from different manufacturers. Even high-end solutions from major brands can be difficult to integrate with third-party hardware. In this project, we successfully merged hardware and software into a single autonomous line — linking robotic arms, a mobile robot, a laser marker, vision systems, and safety devices into one coordinated, training-ready complex.
If you plan to build a similar robotic line for training or real production, buy collaborative robotic arms, buy autonomous mobile robots (AMR) and other automation equipment from Top3DShop — our team of experts will help you choose the right devices, integrate them into a single system, and support your project at every stage.


























Write a comment