
FGF (fused granular fabrication) technology, also known as pellet 3D printing, is becoming more and more popular in industrial manufacturing. Printing directly with plastic granules provides a number of advantages over conventional FDM technology. For certain projects, it turns out to be the only production method that is economically feasible. What are the most suitable applications for FGF printing?
This is Top 3D Shop, and in this article, we will discuss pellet 3D printing technology, its benefits and limitations, and have a look at the equipment used for granular manufacturing.
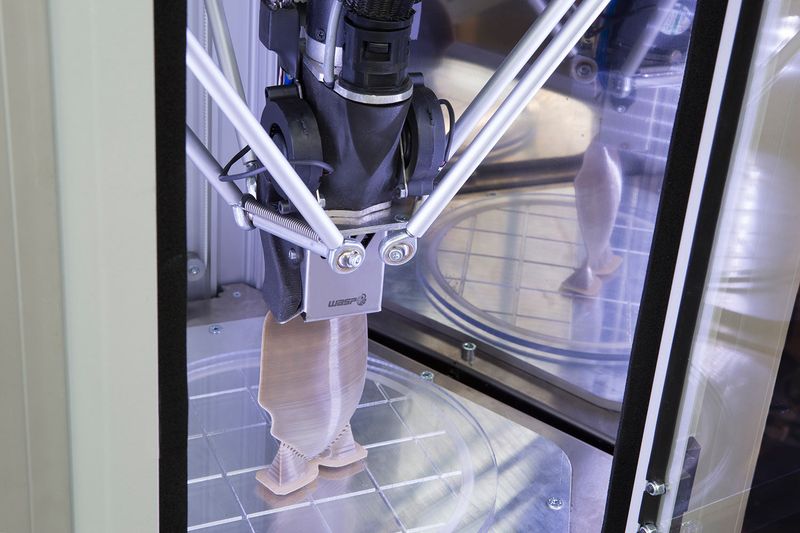

Credit: 3dwasp.com
Printing with pellets is based on the same material extrusion technology as commonly known FDM 3D printing. The difference is in the form of thermoplastic used for building parts and, consequently, a special extruder, designed to process plastic granules instead of FDM filament. While any plastic filament is made from pellets, the idea to skip the stage of filament manufacturing and print directly with granular material is quite obvious. This not only allows cutting material costs, but makes for its better quality, as pellets need to be heated to produce filaments, which leads to certain degradation of thermoplastic properties. Apparently, there are some changes to the printer construction that have to be made to adapt it to a different material type. In FGF 3D printers, pellets are placed into a hopper and delivered to a specialized print head, where they are melted and extruded onto the build plate in a layer-by-layer manner.
The key element of a pellet extruder is a screw that rotates inside a barrel to transport plastic granules from the hopper to the nozzle. The extruder usually has multiple heating zones that melt the plastic into a homogeneous plasticized mass and maintain constant temperature and flow rate for consistent extrusion. Under the pressure created by the rotation of the screw, the molten material is pushed through the nozzle onto the build plate. Pellet extruders generally use larger nozzle sizes than filament ones and provide much higher throughput and up to 200 times faster print speeds.
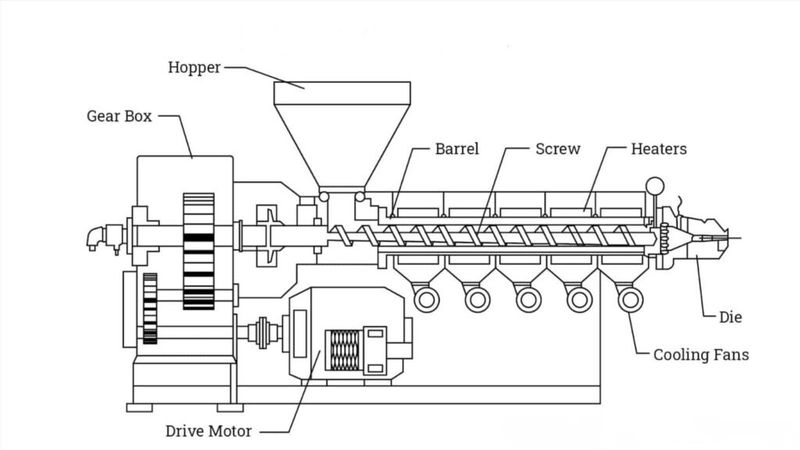
Credit: engineeringlearn.com
Printing directly with pellets allows saving 60 to 90% on the material cost. Besides, there are other notable advantages of using a granular form of plastic. Since this material is used for other manufacturing methods, such as injection molding, the variety of materials in the market is even wider than the choice of FDM filaments. Any thermoplastic suitable for 3D printing can be found in a pelleted form, from consumer PLA and ABS to high-performance engineering-grade PC, PEEK, PEKK, and others. FGF printing also allows for easy creation of custom materials with required properties by using various additives, such as carbon and glass fibers or kevlar for reinforcement, dyes to get a certain color, or other additives to improve thermal and mechanical properties or get the material with fire retardant, magnetic, ESD-safe, and other characteristics.

Credit: piocreat3d.com
Apart from using virgin granular feedstock, FGF technology helps significantly reduce or even eliminate plastic waste by printing with recycled materials, thus saving the environment. Failed prints or removed support structures can be shredded using special equipment and utilized for printing.
Before moving on to FGF printing applications and the list of relevant equipment, let us sum up the benefits and limitations of pellet additive manufacturing compared to FDM 3D printing.
Pros
Lower material cost. As mentioned, pellets generally cost a fraction of the price of the same plastic filament.
Faster print speeds. Due to pellet extruder design with large heating zones and wider nozzle diameters, FGF printers provide much higher throughput and faster print speeds, which is invaluable for industrial manufacturing of large parts and batch production.
Wide material selection. Besides a variety of thermoplastic pellets from different manufacturers in the market, the user can create custom materials with predefined properties as well as print with recycled plastic.
Eco-friendliness. FGF 3D printing allows significantly reducing the amount of plastic waste and carbon footprint, making for a safer environment.

Credit: Piocreat 3D / YouTube
Cons
Lower print resolution. For creating miniature models with a lot of fine details and tight tolerances, it is better to opt for other 3D printing technologies.
Design limitations. Support structures are difficult to build and remove and therefore seldom used in pellet printing. So, parts with complex geometries, overhangs and cavities are better printed on FDM machines.
Lower flow control. Pellet extruders are capable of much higher throughput than filament machines, but they can not provide the same level of flow control. While filament extruders retract the material when moving to a new location, the design of a pellet extruder does not allow for retraction, which can lead to material oozing.
Considering the specifics of pellet 3D printing, its strengths and weaknesses, we see that FGF technology is a great choice when it comes to large-scale manufacturing or series production of parts with relatively simple geometries, where a high level of detail is not a priority. Such industries as aerospace, automotive, marine, construction, and many others can greatly benefit from the use of pellets in production. It also provides furniture and interior designers with the opportunity not only to get their projects to mass production but make them cost-effective.
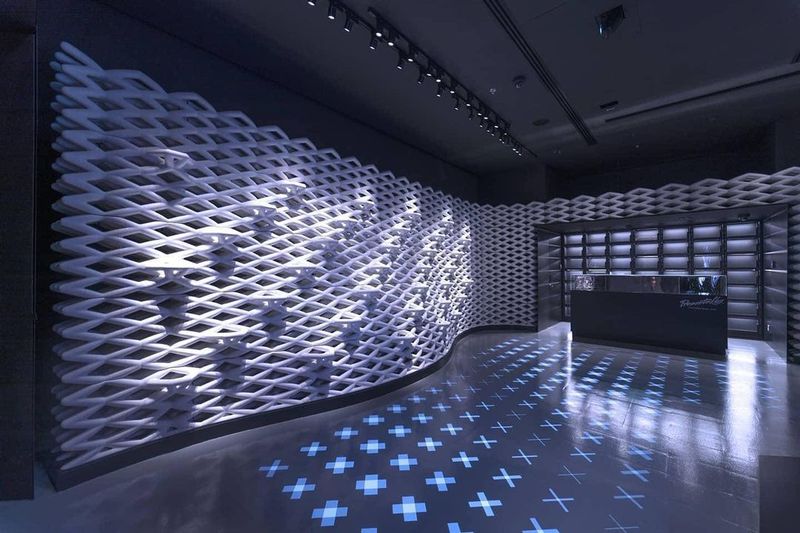

3D printed walls in a flagship store built with the WASP 3MT HDP 3D printer
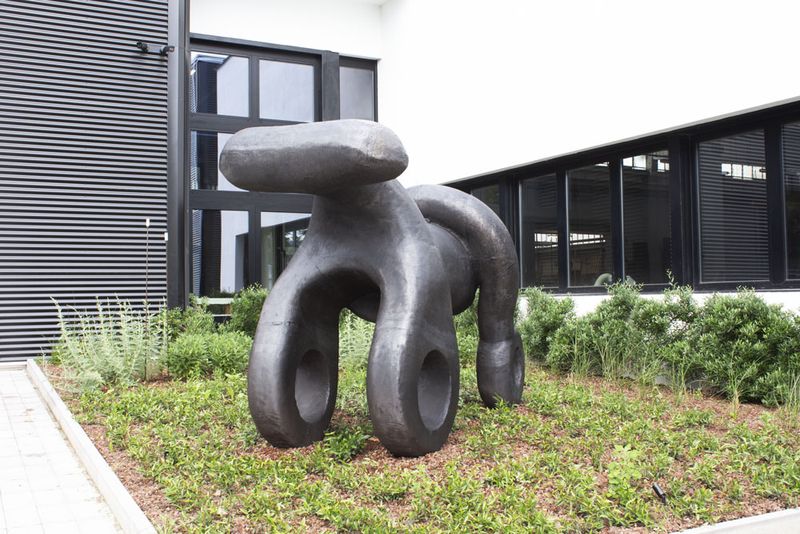

4 x 2.5 m ABS sculpture printed with the Delta WASP 3MT industrial 4.0 3D printer.
Credit: 3dwasp.com
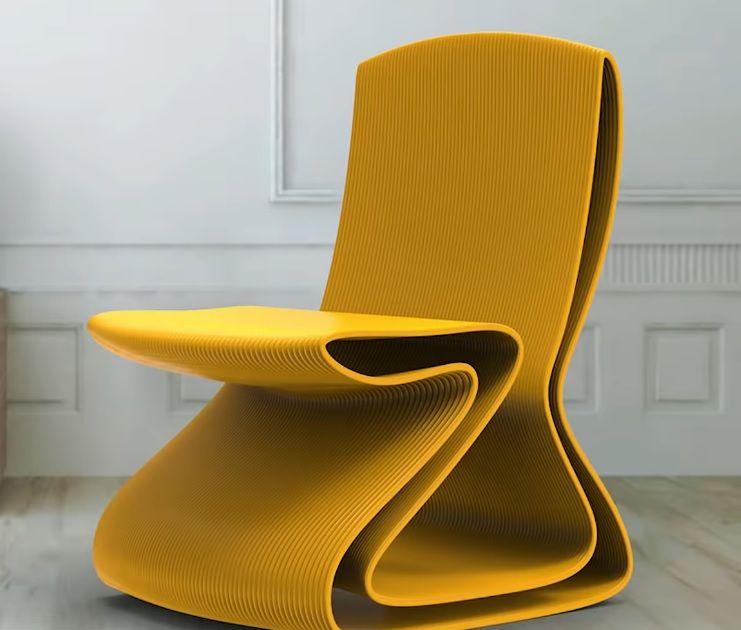

A chair printed with the PioCreat G12 3D printer.
Credit: Piocreat 3D / YouTube
Speaking of environmental benefits of pellet 3D printing, one can remember the Tokyo Olympics-2020, where all 98 Olympic podiums were 3D printed using 24.5 tons of recycled household plastic waste collected throughout Japan for the project. The video below demonstrates the process of podium creation.
For those who want to start printing with granular materials, there are several options. The first one is an FGF 3D printer designed specifically to process pellets. Such machines are usually meant for high-volume industrial manufacturing, big in size and comparatively pricey, although they pay off in a short term due to low material cost and extremely high productivity. Besides, some manufacturers offer compact FGF machines at a reasonable price, which makes them accessible for small businesses. An example of such a device is the Piocreat G5 Pro desktop pellet 3D printer. Below you will find some more Piocreat pellet 3D printers you can buy at Top 3D Shop.
Another company producing equipment for pellet printing is Italian-based WASP. Some of the company’s printers have an interchangeable extruder setup allowing it to print with both pellets and filaments.
One more option to print with pellets is to purchase a dedicated extruder and material feeding system. Pellet extruders can be installed on any large-scale 3D printer or a robotic arm. An example is the Dyze Design Pulsar, a high-flow plastic pellet extruder with three-zone heating and anti-oozing mechanism, capable of throughput of 2.5 kg/h. The extruder can be equipped with an optional automatic feeding system for continuous printing.
FGF technology offers a lot of benefits for industrial printing, compared to conventional FDM manufacturing. Large-scale and batch production becomes much more efficient in terms of time and cost. Allowing for a wide choice of pellets combined with the ability to print with customized and recycled materials, pellet 3D printing is a promising technology that is sure to find its application in a great number of industries.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment