
If you've been using your 3D printer long enough, you probably know its advantages and shortcomings. If the drawbacks become too tangible over time, then your printer may need to be upgraded, reconfigured, and reflashed.
Read the article to learn how to reflash your 3D printer and restore its ability to run smoothly.
Source: all3dp.com
Firmware is the "intelligence" of a 3D printer — its main program, which allows processing G-code commands received from the slicer, implementing them into specific actions and characteristics of actions performed by the hardware of the device. For instance, the software sends the G-code command “G1 X50 Y50”. The printer firmware determines the polarity, voltage, and duration of pulse to the motor drivers needed to move the extruder to X = 50 mm and Y = 50 mm, after which the firmware sends electrical signals to these drivers. In the same way, the firmware converts the G-code commands into the actions of the cooler, heaters, and other elements of the printer.
The method of reflashing a 3D printer is comparable, for example, with manually flashing a smartphone. If you are familiar with this kind of work, you must know how much effort and time it can take to get the perfect result. If you have not dealt with such specific tasks, then to reflash the printer, you should contact a skilled specialist or carefully study the experience of colleagues and strictly follow their instructions.
Source: all3dp.com
If the stability of operation in your 3D printer begins to deteriorate, it doesn't necessarily mean that your device needs reflashing. It is possible that typical problems with the equipment such as overheating of the extruder or the motherboard and drivers are caused by mechanical malfunction and wear. It may be a disconnection between elements connected through ribbon cables, or clogged nozzles, contamination of the extruder, wear of printer components, loosening of screw connections, stretching drive belts. It is enough to eliminate the source of the problem, and the stable operation will be restored.
However, it can be that a 3D printer lacks the necessary functions or elements. For example, a heated bed for the Wanhao i3 Mini, a camera for the Anycubic Chiron, or a HEPA filter for the Anet resin printer. In this case, you can equip your device with additional components: fans, motors, heaters, temperature sensors. It is not difficult to install new elements, but how do you manage them? This will require reflashing the printer.
Reflash can also solve typical problems arising in case of software malfunctions:
Source: all3dp.com
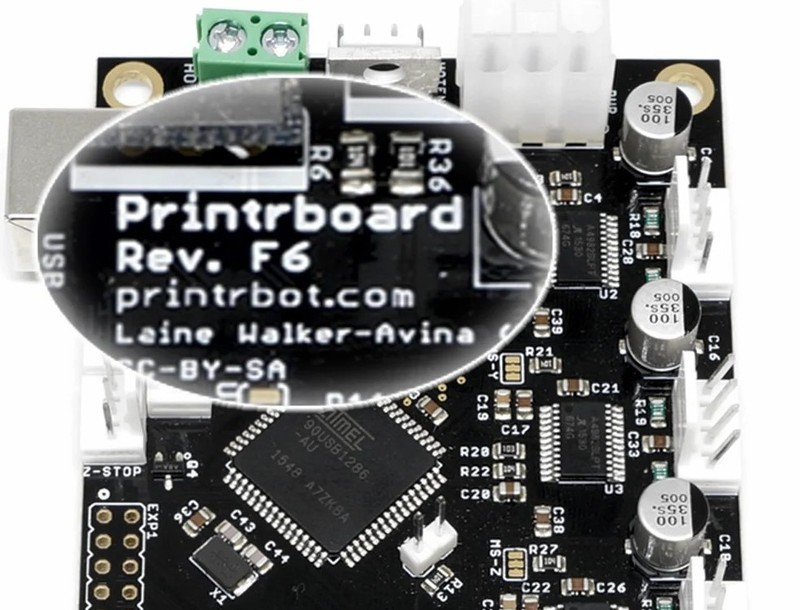
Before you start reflashing your 3D printer, you need to determine the manufacturer of the controller board. This information is engraved or printed directly on the motherboard itself. Most often, budget FDM printers are equipped with Arduino boards. There are also devices that use Smoothie, BeagleBone, and Duet boards, as well as the printer manufacturer's proprietary electronic components. Board manufacturers publish the latest firmware versions on their official websites. For example: Arduino, Wanhao 3D printer, Phrozen.
Please note that the installation of third-party firmware from unknown sources can lead to equipment damage and will definitely lead to the loss of warranty.
Source: all3dp.com
To experiment with the firmware, we recommend using an additionally purchased controller, which you can lose and not damage your printer.
It is recommended to only update the firmware of the factory boards as new versions appear on the official website. However, even with the appearance of the latest version, reflashing may be redundant. As practice shows, if a 3D printer properly performs its tasks, you should not interfere with it. Popular wisdom says: "If it ain't broke, don't fix it."
It goes without saying that you also have to know for sure that the firmware is suitable for the controller. This information can be found on the website of the manufacturer of the printer or board, as well as on the forums for users of that printer.
Source: all3dp.com
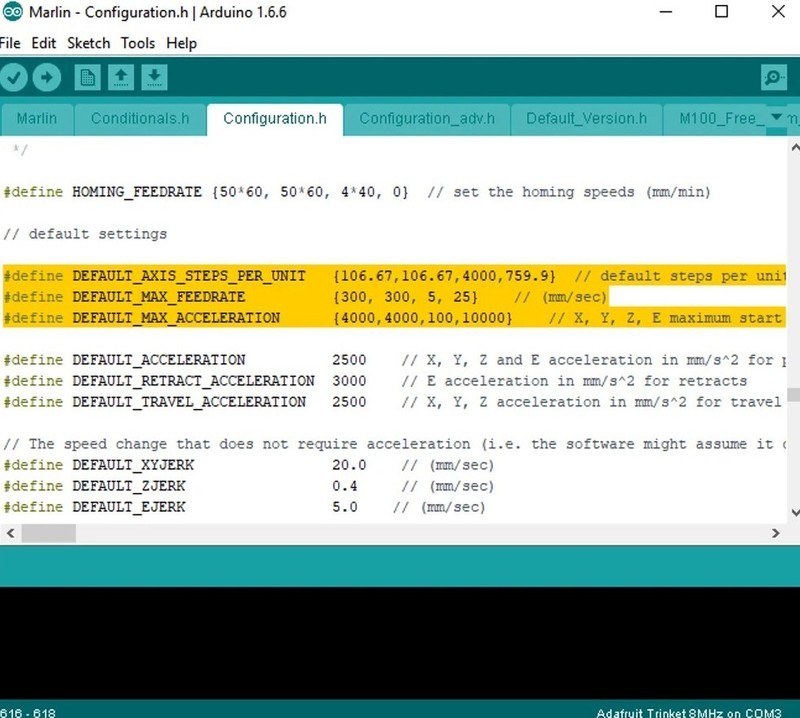
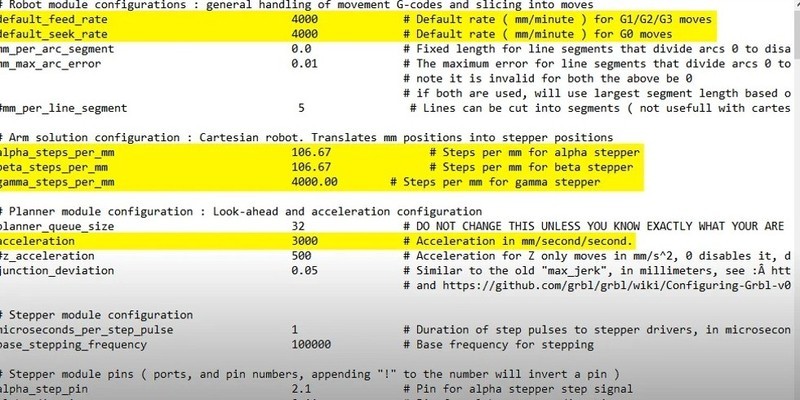
When the new version of firmware is downloaded to the computer, the user cannot manually edit the configuration file. In the Marlin and Repetier source codes, files edited have a special extension, for example, .h. It is recommended to save a copy of the unmodified firmware version on your computer. This will save time if you have to drop the edited file. After changes to the configuration file are made, the new values should be saved, after which you can start reflashing.
Common variable parameters are as follows:
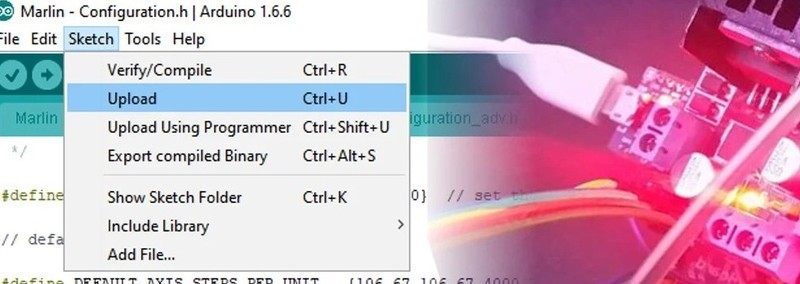
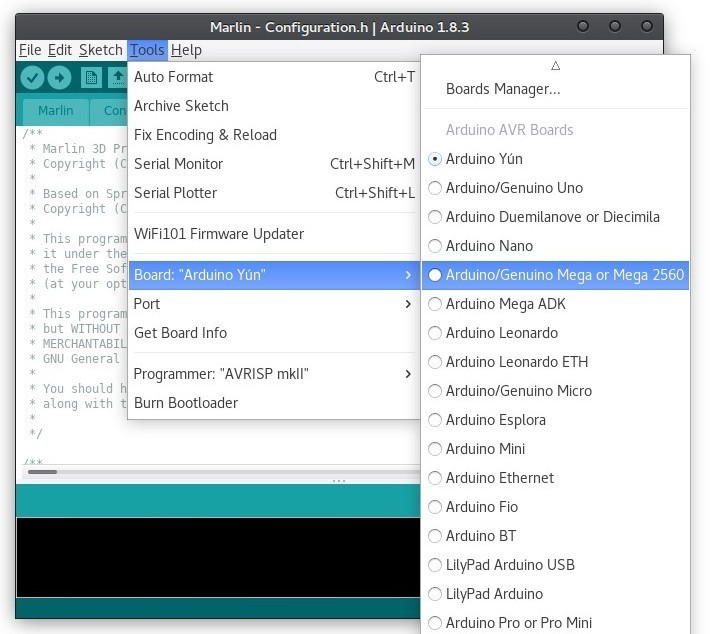
The firmware is installed on the printer from the computer to which the device is connected. It is important to understand that installation is the process of creating (compiling) the source code of the firmware and loading it into the microcontrollers of the control board. In the program (the example shown in the screenshot below demonstrates Marlin), you need to specify the board model (Arduino Mega 2560) and the port (connected 3D printer). In order not to be mistaken with the port, it is better to leave only one 3D printer connected at the time of reflashing.
Source: matterhackers.com
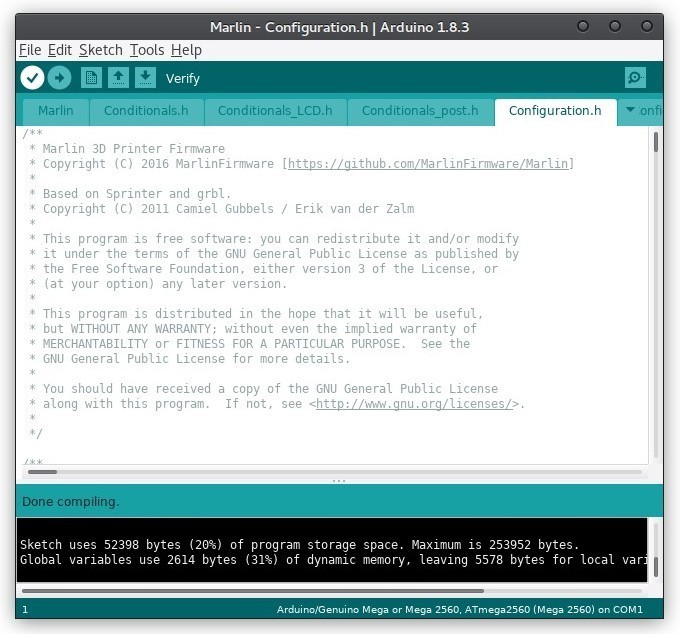
Then you need to compile the firmware files, that is, to convert the human-readable code into the binary one. This is an automatic process. If everything is done correctly, a file will be created to be downloaded to the printer. Otherwise, the program will display an error message, which will require changing the configuration parameters or recompiling the unedited version of the firmware.
Source: matterhackers.com
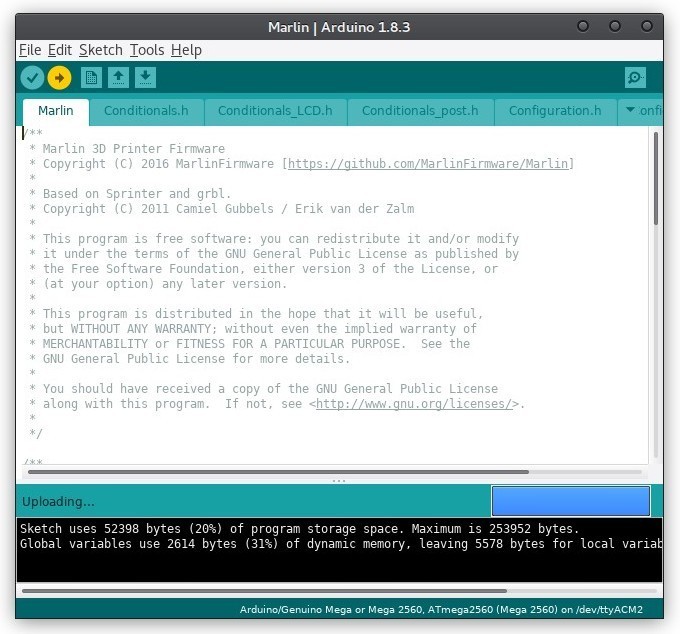
The compiled firmware is loaded onto a 3D printer. The process takes a few minutes, after which the 3D printer will automatically reboot.
Source: matterhackers.com
Marlin is a popular 3D printer firmware compatible with 8- and 32-bit boards. The firmware provides the user with a wide range of settings. For example, the display interface controller has a choice of 30 languages. You can download the latest and some previous versions of the firmware from the project's website.
Repetier-Firmware is created by the team that made the popular Repetier-Host slicer. The firmware is compatible with 8-bit boards and 32-bit boards with AVR controllers (Arduino Due and RADDS). It allows for online editing of the configuration file.
RepRap Firmware is developed for 32-bit chips based on AVR controllers.
Smoothieware is similar to RepRap Firmware. It works only on a limited number of boards, the main ones being the Smoothieboard and Azteeg X5 Mini.
Reflashing a 3D printer is possible for most models using the FDM/FFF technology and is necessary if a malfunction is detected due to incorrect operation of the electronics or the hardware is being upgraded. Before starting to reflash, the user has to determine what type of controller board is installed in the printer. Then it is necessary to find a compatible firmware and download it to the device.
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
Write a comment